大环内酯类抗生素是非常重要的一类抗菌化合物,广泛用于人类和兽医的治疗和预防[1]。泰乐菌素(tylosin,TYL)是最常用的预混大环内酯类抗生素,对革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性细菌、支原体、巴斯德氏菌以及衣原体具有很高的活性[2]。它们被广泛用于动物生产中,以预防和治疗家畜的肠道和呼吸道感染[3-4]。滥用抗生素可能会在可食用的动物组织和牛奶中留下残留物,对消费者健康造成不利的影响。因此,许多国家禁止在饲料添加剂中使用TYL,它于1998年在欧盟被禁止。在中国,可食用动物组织中TYL的最大残留限量(maximum residue limit,MRL)规定为50 μg/kg(牛奶)和200 μg/kg(肌肉组织)[5]。牛奶中TYL的MRL也是巴西农业、畜牧和食品供应部在牛奶中TYL残留法规中采用的MRL。这与欧盟和美国食品药品监督管理局(Food and Drug Administration,FDA)要求的MRL一致[6-7]。为了评估TYL的残留量,需要灵敏的分析方法以确保低浓度下的测定。文献揭示了几种测定肌肉组织中TYL残留的方法,如HPLC[8-9]、薄层色谱[10]、LC-MS/MS[11-12]和酶联免疫吸附法(enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)分析[13]。尽管这些方法准确可靠,但它们昂贵,预处理(尤其是提取和纯化)复杂且耗时,因此不适用于现场测试或常规分析的高通量分析筛查[14]。从实践的角度来看,开发一种简单,低成本,省时的筛选技术至关重要[15]。
自1980年初期发展以来,侧流免疫层析测定技术已获得广泛认可[16],其受欢迎的主要原因是测试设计的简单性。侧流免疫层析测定装置紧凑且易于携带,大多数不需要外部试剂即可获得结果,添加液体样品将启动并完成测试,结果快速且易于解释,通常无需借助仪器,检测试纸条的制造相对容易且便宜。近年来,侧流免疫层析试纸被用作检测激素[17]、病毒(艾滋病毒、乙肝和丙型肝炎、新冠病毒)[18-20]、细菌[21]和寄生虫等抗原的流行诊断工具[22]。对于较小的分析物,可以使用竞争性ELISA测定[23],检测试剂通常是针对分析物的胶体金标记抗体。捕获线通常是与固定在膜上的载体蛋白缀合的分析物。样品中的分析物将与固定在膜上的分析物竞争,从而与检测抗体结合。样品中存在的分析物越多,它将越有效地阻止胶体金标记抗体的捕获。因此,样品中分析物数量的增加将导致读出区域中信号的减少[24-25]。到目前为止,竞争性剥离测试主要用于检测小分子物质(半抗原),尤其是在动物饲养中滥用的药物。这种竞争性测定的检测极限可以达到ppb水平(每克样品分析物的纳克级数)。
在这项工作中,针对TYL的免疫原,产生了TYL的特异性单克隆抗体(monoclonal antibodies,mAb)。在此基础上,开发了一种单步免疫色谱测试条,用于检测牛奶中的TYL残留性。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料与试剂
氯金酸和酪蛋白,American Sigma Company;牛血清白蛋白(bovine serum albumin,BSA),American Amresco Company;辣根过氧化物酶(horseradish peroxidase,HRP)标记的山羊抗小鼠免疫球蛋白G(immunoglobulin G,IgG),American Jackson Laboratory;聚氯乙烯(polyvinyl chloride,PVC)塑料片、血液滤过膜、吸收纸,上海金标生物技术有限公司;硝酸纤维素(nitrocellulose membrane,NC)膜,American Millipore Company。
1.2 仪器与设备
Forma 371 Steri-Cycle酶标仪,Thermo Fisher;XYZ Biostrip分配器、CM 4000切割机,美国加利福尼亚州Bio-Dot。
1.3 免疫原的偶联
通过碳二亚胺法制备该程序中的TYL。将5 mg的TYL溶解在磷酸盐缓冲液(phosphate buffer,PBS,pH 7.0)中,然后加入10 mg的碳二亚胺化合物。将混合物在黑暗中于4 ℃搅拌约6 h。将BSA或卵清蛋白(ovalbumin,OVA)溶解在PBS缓冲液中,并加入混合物中。TYL与BSA或OVA的摩尔比为25∶1。将免疫原BSA-TYL(OVA-TYL)在室温下搅拌过夜,并用PBS透析约3 d [26]。通过紫外光谱和SDS-PAGE分析免疫原。免疫原在-20 ℃的条件下保存。
1.4 单克隆抗体生产
用3种免疫原中的每一种免疫5只雌性BALB/c小鼠(6周龄)(每只小鼠的剂量为50 μg蛋白),以产生mAb。每2周使用弗氏完全佐剂中的免疫原乳剂对小鼠进行皮下免疫。第三次免疫后从每只小鼠收集血清,并通过ELISA监测抗体滴度。处死具有最高抗体滴度的小鼠,并使用SP2/0骨髓瘤细胞融合脾细胞。融合的细胞在HAT培养基中繁殖。融合后,使用HAT培养基针对选择未融合的细胞。在选择融合细胞之后,将HAT培养基替换为HT培养基。使用非竞争性间接ELISA筛选生长中的杂交瘤细胞中抗体的产生。通过有限稀释法将产生针对TYL的特异性mAb的杂交瘤亚克隆2次。收集亚克隆的杂交瘤细胞,离心并在液氮中冷冻[20]。用饱和硫酸铵沉淀法纯化杂交瘤小鼠的腹水,并用于间接竞争ELISA(icELISA)。
1.5 间接竞争ELISA
微量滴定板的每个孔均涂有100 μL包被抗原。将板在4 ℃下孵育过夜,然后用200 μL封闭缓冲液(0.01 mol/L含50 g/L BSA的PBS)封闭。随后将50 μL最佳抗体稀释液和50 μL具有连续稀释度的TYL标准液添加到孔中,并将滴定板在37 ℃下孵育30 min。洗涤后再加入100 μL稀释的山羊抗小鼠IgG-HRP溶液,并将板在37 ℃下孵育30 min。洗涤后,加入100 μL 3,3′,5,5′-四甲基联苯胺(3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine,TMB)底物(在0.05 mol/L柠檬酸缓冲液中,pH 4.5 的10 g/L TMB和H2O2),在37 ℃ 孵育10 min后,反应用2 mol/L H2SO4终止反应。然后,用在450 nm处测量吸光度OD450值。为了间接比较不同的校准曲线,将OD450值转换为相应的测试抑制率,如公式(1)所示:
测定抑制率![]()
(1)
式中:B,OD450值;B0,非竞争性抗原OD450值;Bck,阴性对照OD450值。
1.6 胶体金标记单克隆抗体的制备
通过用10 g/L柠檬酸钠控制还原氯化金来制备平均直径为15 nm的胶体金。简而言之,将50 mL的0.1 g/L氯化金三水合物的超纯水溶液(Millipore,美国)加热至沸腾,然后在搅拌的同时添加1 mL的10 g/L柠檬酸钠溶液。颜色从浅黄色变为亮红色后,将溶液再煮沸5 min,以完成氯化金的还原。用碳酸钠(0.2 mol/L)将胶体金溶液的pH值调节至9.0。通过以下步骤确定最佳的蛋白质标记浓度[27]:将25 μL抗-TYL mAb溶液与25 μL胶体金溶液混合。将混合物在室温下孵育15 min,然后添加100 μL的100 g/L NaCl溶液。用于胶体金标记的mAb的最佳浓度是不改变颜色的最低mAb溶液浓度。在20 mmol/L硼酸钠(pH 9.0)中加入1 mL 100 g/L BSA溶液后,将混合物在室温下再孵育10 min,然后在10 ℃下通过重复离心(25 000×g)洗涤标记的mAb用含有10 g/L BSA和1 g/L叠氮化钠的20 mmol/L硼酸钠(pH 9.0)处理30 min。沉淀物重悬在洗涤缓冲液中,并保存在4 ℃以便使用[20]。
1.7 TYL试纸条的组装
免疫层析卡包括样品垫、共轭垫、NC膜、吸收垫、PVC底板以及检测线和质控线,并在其两端覆盖有彩色膜。TYL与BSA连接,然后用作检测线捕获试剂(BSA-TYL)。将山羊抗小鼠IgG用作捕获试剂,在NC膜上进行测试。金标抗体用量按照上述优化后的条件加入96孔板的微孔,在40 ℃下干燥1 h后,将膜密封并在室温下在干燥条件下贮存。通过用20 mmol/L含87.5 g/L蔗糖,87.5 g/L BSA,0.6 mol/L NaCl的硼酸钠缓冲液(pH 8.0)将胶体金标记的mAb稀释为TYL制备缀合物溶液。10 mmol/L EDTA和1 g/L 叠氮化钠的终质量浓度为2 μg/mL。将7 mm×300 mm 玻璃纤维(Millipore,MA,USA)浸入共轭溶液中,制成共轭垫,然后在56 ℃下干燥1 h。样品垫和吸收垫是由无纺布的100%纯纤维素制成的[25,28]。使用切割机将主卡切成3 mm宽的条。然后将条带在干燥剂凝胶存在的情况下密封在塑料袋中,并保存在4 ℃下。
1.8 测试程序和原则
牛奶样品在5 000 r/min下离心15 min以去除脂肪。将一块测试条插入80 μL标准样品中10 s,然后将其平放以使溶液迁移。胶体金标记的抗TYL mAb被固定在膜上的BSA-TYL捕获,形成一条清晰的红色测试线。过量标记的抗TYL mAb进一步迁移并被形成对照系的山羊抗小鼠IgG抗体捕获,完成测试需要10 min。如果样品中存在TYL,它将与测试线上的固定BSA-TYL竞争,以结合有限量的胶体金标记的抗TYL mAb(图1)。
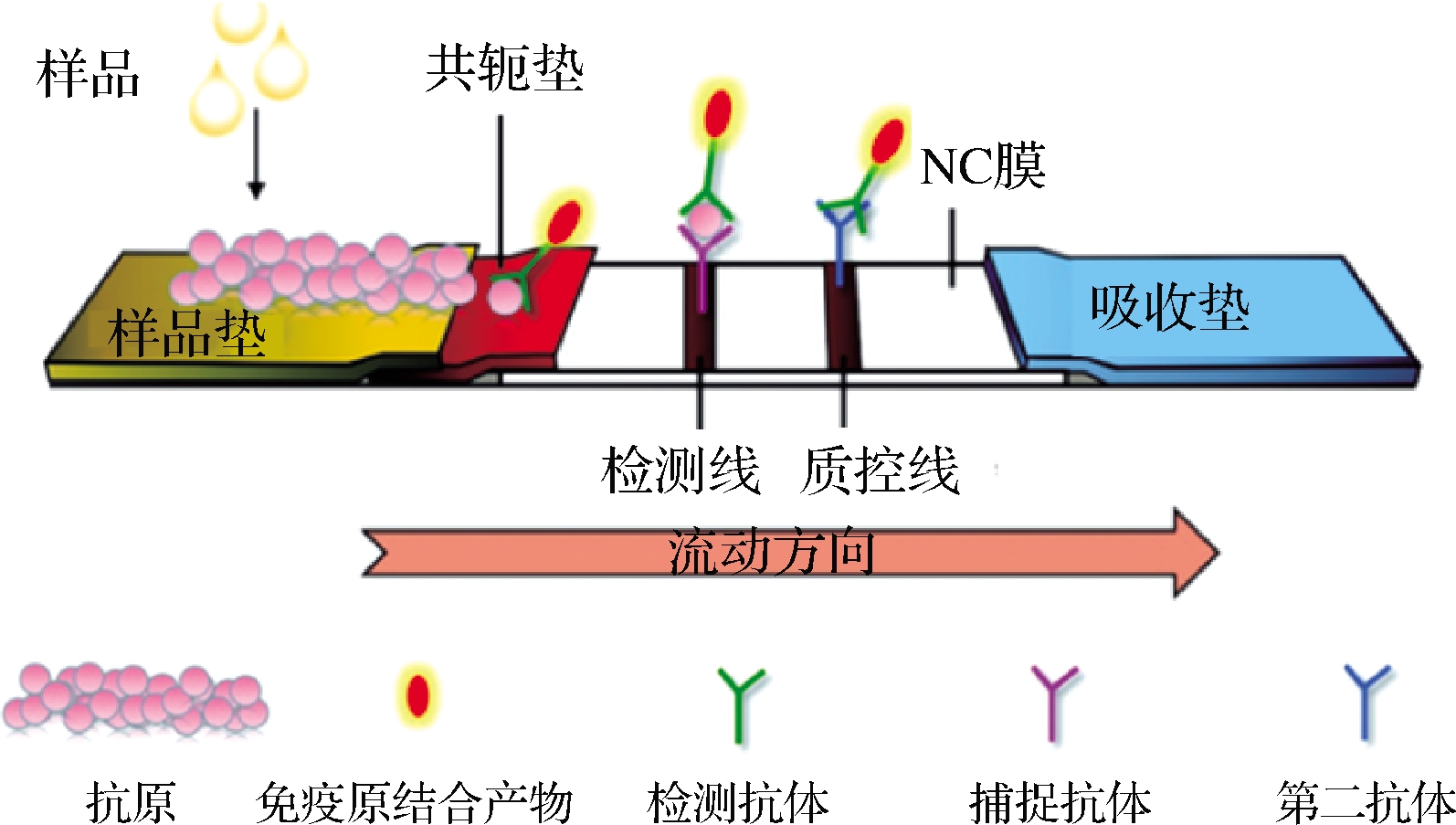
图1 胶体金免疫层析试纸条检测原理示意图[29]
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the detection principle of colloidal gold immunochromatographic test strips[29]
1.9 统计分析
使用统计软件SPSS 11.0和数据处理系统14.0(data processing system,DPS)进行统计[30]。数值表示为平均值±标准差。所有数据均适用于分析,无需任何转换。
2 结果与分析
2.1 mAb对TYL的影响
通过ELISA法评估了针对TYL的单克隆抗体mAb对TYL的影响。抗体效价表示为最大稀释度的倒数,最大稀释度产生的OD450值比阴性对照高2.1倍。结果表明,抗体效价为2.56×10-5(图2)。将IC50(IC50是捕获在测试线上的胶体金标记的抗TYL mAb 50%抑制的浓度。交叉反应性表示为竞争者的IC50浓度除以TYL的百分比)评估为50%测试抑制率下的TYL浓度。结果表明,IC50为4.609 1 ng/mL。通过用PBS稀释TYL来建立ELISA的标准抑制曲线(图3)。
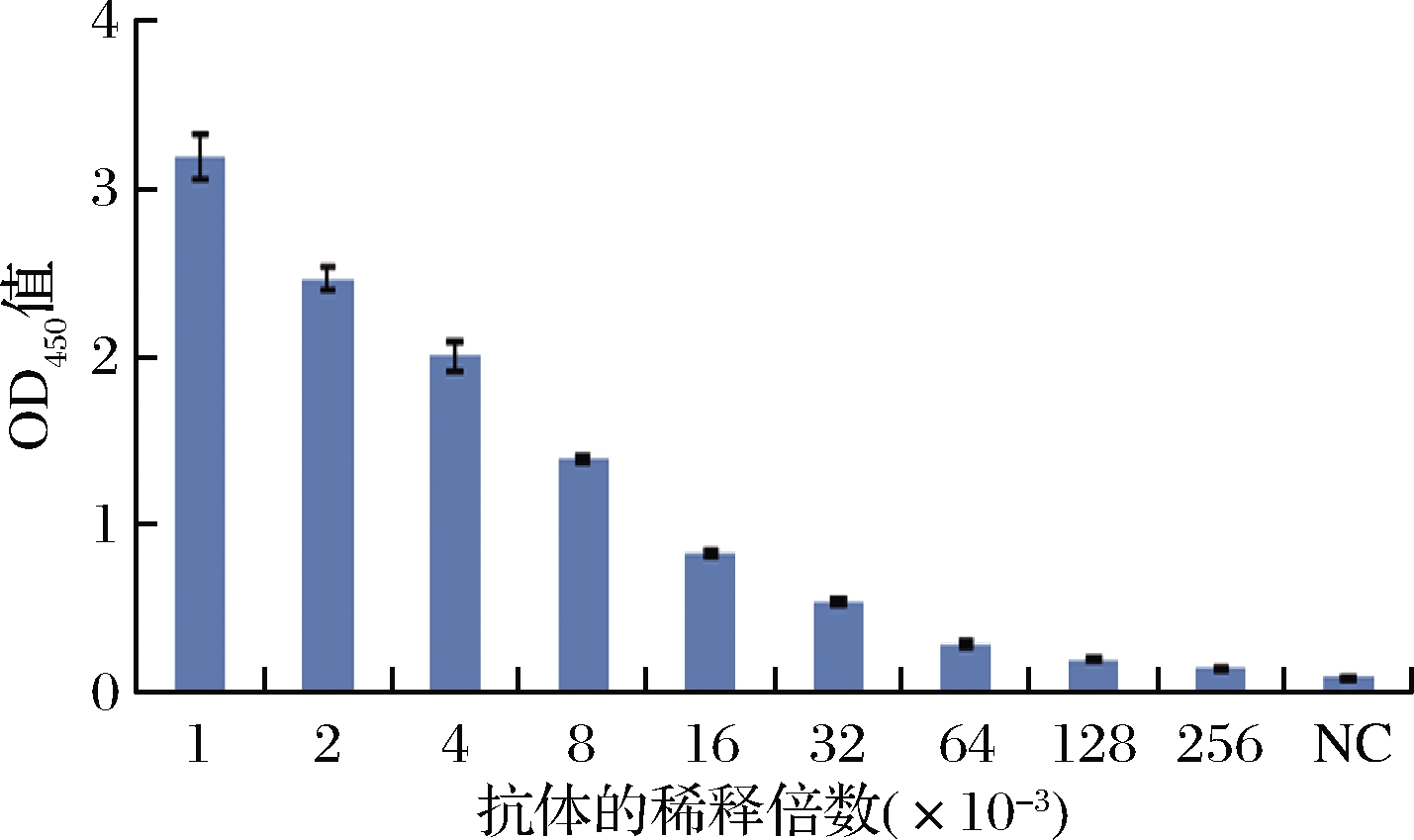
图2 抗TYL抗体滴度
Fig.2 Anti-TYL antibody titer
注:NC为阴性对照
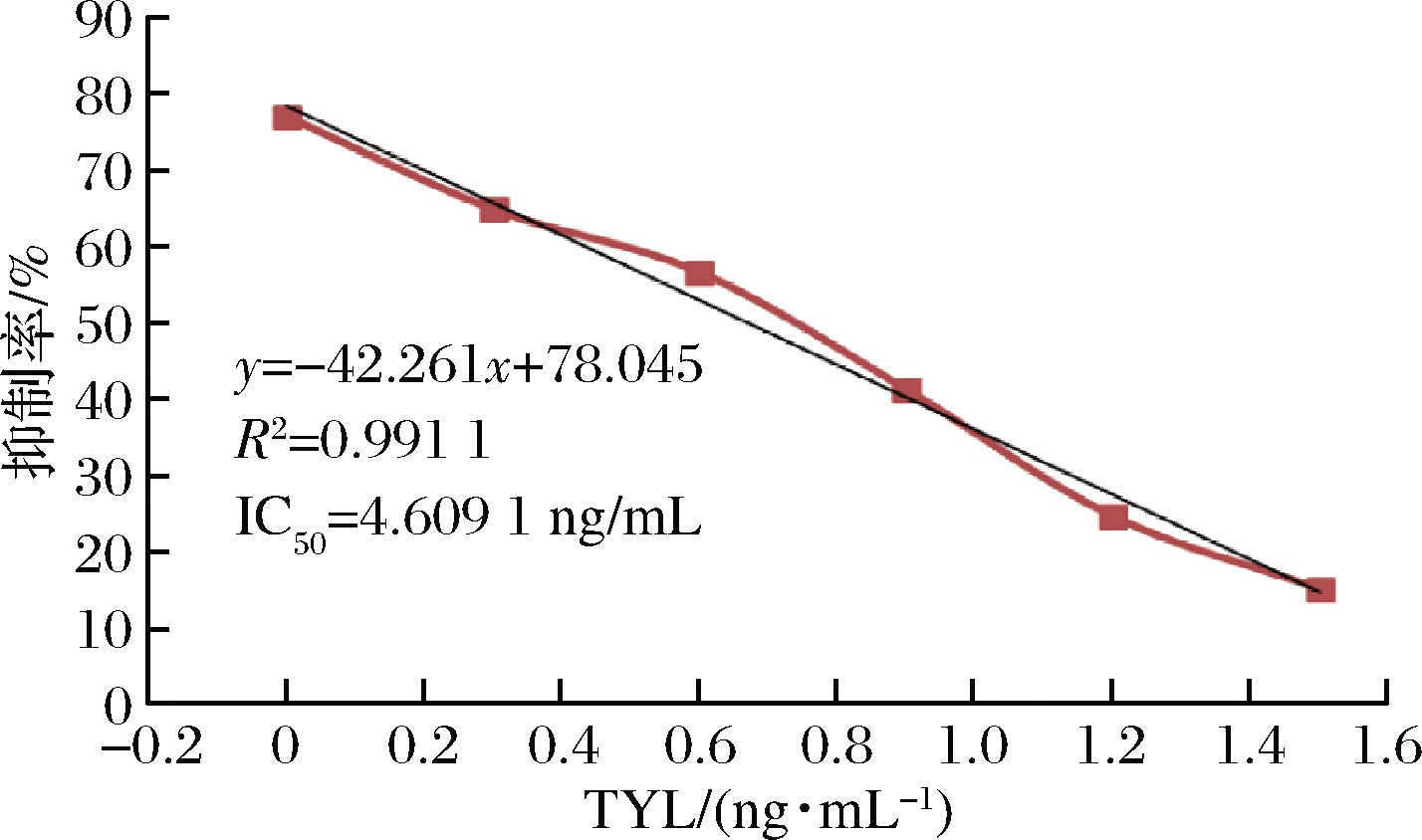
图3 icELISA的抑制曲线
Fig.3 Inhibitory curves by icELISA
注:标准曲线的标准质量浓度为1、2、4、8、16、32 ng/mL, 以标准样品取对数计算
2.2 试纸的灵敏度
通过测试TYL标准样品来预测试纸条的灵敏度。用读数仪扫描检测线。G/Peak和G/D×相对光密度(relative optical density,ROD)的面积随着标准样品中TYL浓度的增加而降低(图4和表1)。
使用无污染牛奶测定了检出限(limit of detection,LOD)。LOD以阴性样品20次测定结果的平均值加3倍标准偏差计算。与阴性对照(NC)相比,LOD对应于G/D×Area-ROD下降10%的浓度。结果表明,使用扫描仪计算出的LOD为1.563 4 ng/mL,而使用眼睛计算出的LOD为10 ng/mL。计算其IC50为7.836 2 ng/mL。
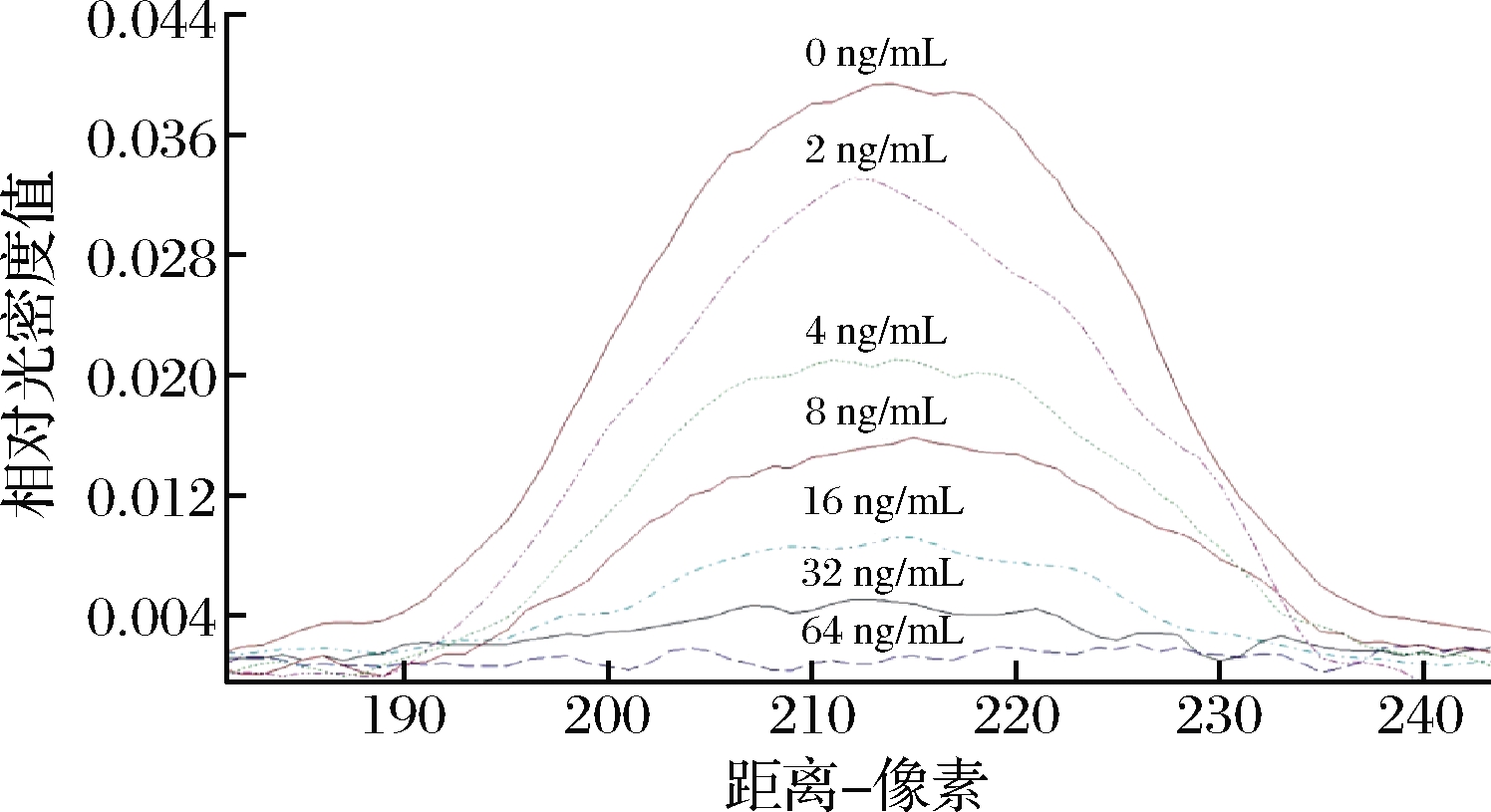
图4 标准样品的ROD曲线
Fig.4 ROD curves of standard samples
注:使用测试条测试了0、2、4、8、16、32、64 ng/mL的标准TYL样品; 用TSR3000膜条读取器扫描测试线(309 mm×188 mm,分辨率72×72)
表1 G/Peak和G/D×标准样品测试线的ROD面积
Table 1 G/Peak and G/D×Area of the ROD of test lines of standard samples
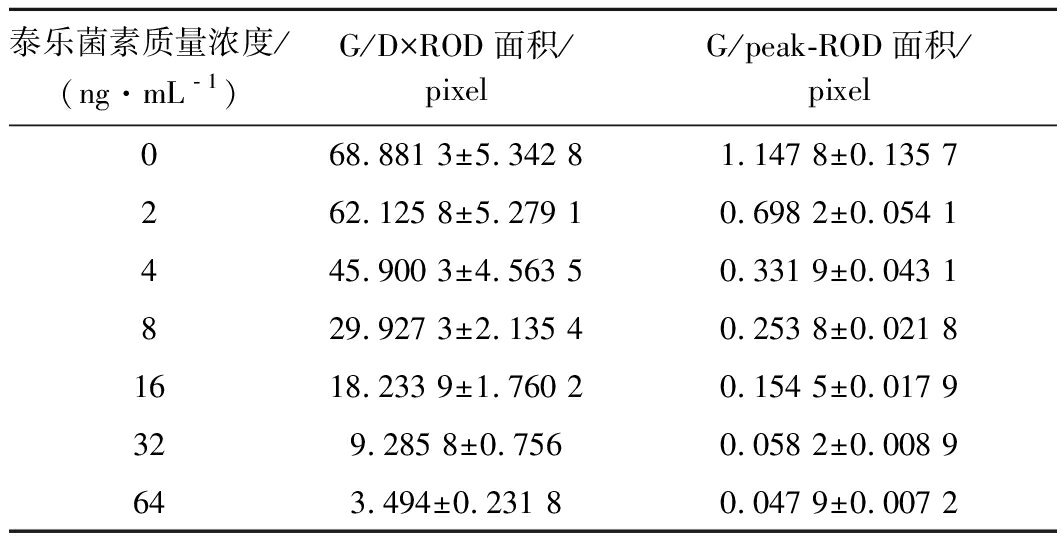
泰乐菌素质量浓度/(ng·mL﹣1)G/D×ROD面积/pixelG/peak-ROD面积/pixel068.881 3±5.342 81.147 8±0.135 7262.125 8±5.279 10.698 2±0.054 1445.900 3±4.563 50.331 9±0.043 1829.927 3±2.135 40.253 8±0.021 81618.233 9±1.760 20.154 5±0.017 9329.285 8±0.7560.058 2±0.008 9643.494±0.231 80.047 9±0.007 2
2.3 试纸的特异性
根据四参数对数方程,抗TYL mAb对TYL和其他兽药的IC50和反应性如表2所示。计算得出TYL的IC50为7.836 2 ng/mL,而其他兽药(包括替米考星、螺旋霉素、交沙霉素、罗红霉素、红霉素、阿奇霉素、磺胺甲氧二嗪、克仑特罗、链霉素和莱克多巴胺)IC50值均>3 000 ng/mL。近年来,许多研究人员开发了ELISA方法来检测动物尿液和组织中的TYL[5,31-32]。众所周知,这种方法至少需要3~4 h才能完成。相反,本发明的免疫层析侧流试纸条是一步测定,需要的专业人员和实验仪器少得多。此外,就潜在的交叉反应性而言,与检测TYL残基的多克隆抗体相比,单克隆抗体似乎是更好的解决方案。
2.4 试纸和HPLC之间的比较研究
作为比较任务,HPLC分析[27]被用作鉴定和定量牛奶中TYL的确认方法。从河南省的10个农场中随机抽取10个有代表性的测试样品。结果如表3所示。与HPLC检测相比,期望的最小符合率<15%。
表2 抗TYL单抗与其他兽药的反应性
Table 2 Reactivity of anti-TYL mAb with other veterinary drugs
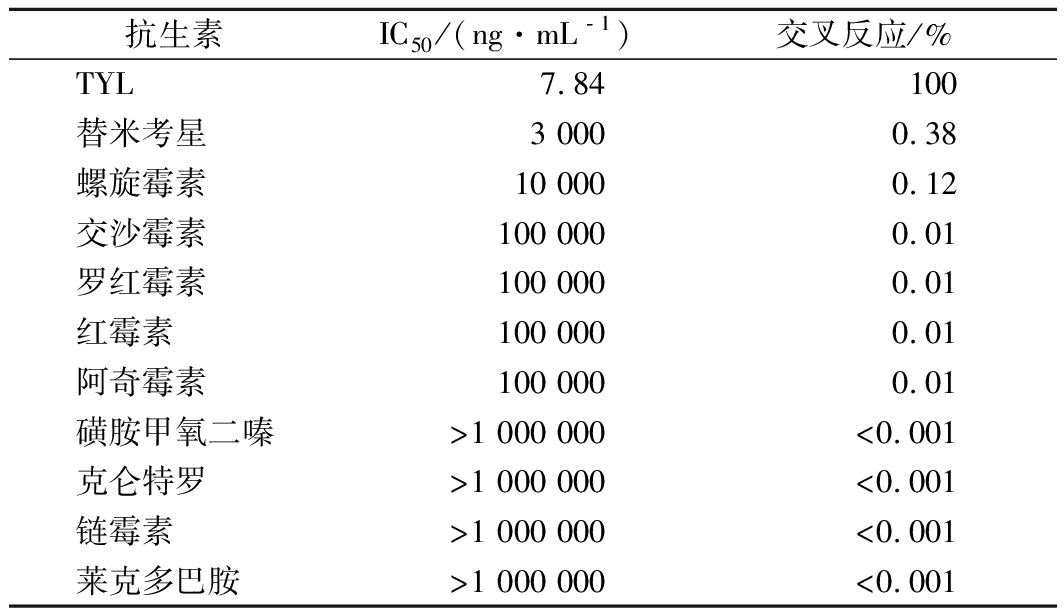
抗生素IC50/(ng·mL﹣1)交叉反应/%TYL7.84100替米考星3 0000.38螺旋霉素10 0000.12交沙霉素100 0000.01罗红霉素100 0000.01红霉素100 0000.01阿奇霉素100 0000.01磺胺甲氧二嗪>1 000 000<0.001克仑特罗>1 000 000<0.001链霉素>1 000 000<0.001莱克多巴胺>1 000 000<0.001
尽管发现HPLC、ELISA和试纸条都适合分析生物样品中的TYL残留,但ELISA和试纸条更为灵敏。当样品中存在高浓度的TYL时,HPLC和试纸条给出的结果一致或几乎相同,而当样品中存在低浓度的TYL时,其读数却不同(表3)。原因是TYL的量已达到定量极限。在TYL浓度低于HPLC定量限的条件下,测试条是分析TYL残留的更好选择。
表3 用试纸条和HPLC分析检测牛奶中TYL 残留的测试结果比较
Table 3 Comparison of testing results with test strips and HPLC analysis for detection of TYL residues in milk
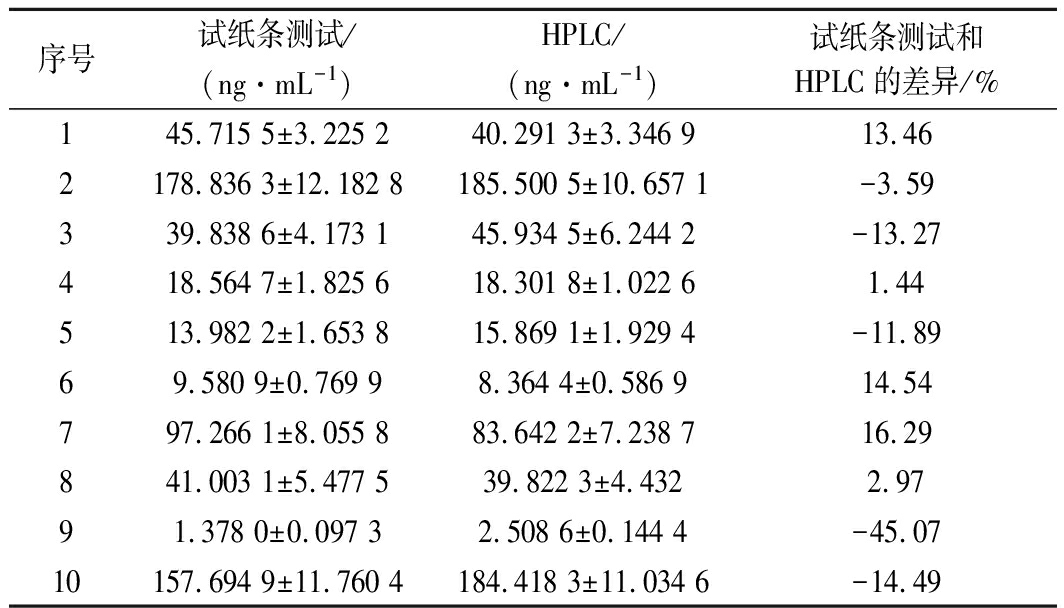
序号试纸条测试/(ng·mL-1)HPLC/(ng·mL-1)试纸条测试和HPLC的差异/%145.715 5±3.225 240.291 3±3.346 913.462178.836 3±12.182 8185.500 5±10.657 1-3.59339.838 6±4.173 145.934 5±6.244 2-13.27418.564 7±1.825 618.301 8±1.022 61.44513.982 2±1.653 815.869 1±1.929 4-11.8969.580 9±0.769 98.364 4±0.586 914.54797.266 1±8.055 883.642 2±7.238 716.29841.003 1±5.477 539.822 3±4.4322.9791.378 0±0.097 32.508 6±0.144 4-45.0710157.694 9±11.760 4184.418 3±11.034 6-14.49
3 结论
本文以牛奶中的TYL为免疫原,成功开发了使用TYL特异性mAb的侧流胶体金免疫层析试纸条。通过和HPLC、ELISA检测方法的比较,发现试纸的LOD为1.563 4 ng/mL,IC50为7.836 2 ng/mL,与ELISA的检测结果有良好的符合率,该指标完全可以满足国家的最低标准要求。结果表明,它对牛奶样品中TYL残留的检测具有很高的特异性和灵敏度。特别是,无需特殊设备,即可在20 min 内获得结果。综上所述,这种牛奶中的TYL快速检测方法,对于牛奶饮用安全性提供了保障。
[1] NASR J J, SHALAN S, BELAL F.Simultaneous determination of tylosin and josamycin residues in muscles, liver, eggs and milk by MLC with a monolithic column and time-programmed UV detection:Application to baby food and formulae[J].Chemistry Central Journal, 2014, 8(1):1-9.
[2] MECHESSO A F, PARK S C.Tylosin exposure reduces the susceptibility of Salmonella Typhimurium to florfenicol and tetracycline[J].BMC Veterinary Research, 2020, 16(1):22.
[3] KIM J, GUEVARRA R B, NGUYEN S G, et al.Effects of the antibiotics growth promoter tylosin on swine gut microbiota[J].Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 26(5):876-882.
[4] ABDALLAH A, ZHANG P, ZHONG Q Z, et al.Application of traditional Chinese herbal medicine by-products as dietary feed supplements and antibiotic replacements in animal production[J].Current Drug Metabolism, 2019, 20(1):54-64.
[5] PENG D P, FENG L, PAN Y H, et al.Development and validation of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for monitoring organoarsenic compounds in edible chicken and pork and feed[J].Food Chemistry, 2016, 197:821-828.
[6] DE FREITAS A G, DE MAGALH ES B E, MINHO L A, et al.FTIR spectroscopy with chemometrics for determination of tylosin residues in milk[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2021, 101(5):1 854-1 860.
ES B E, MINHO L A, et al.FTIR spectroscopy with chemometrics for determination of tylosin residues in milk[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2021, 101(5):1 854-1 860.
[7] SEHATI N, DALALI N, SOLTANPOUR S, et al.Extraction and preconcentration of tylosin from milk samples through functionalized TiO2 nanoparticles reinforced with a hollow fiber membrane as a novel solid/liquid-phase microextraction technique[J].Journal of Separation Science, 2014, 37(15):2 025-2 031.
[8] CIVITAREALE C, FIORI M, BALLERINI A, et al.Identification and quantification method of spiramycin and tylosin in feedingstuffs with HPLC-UV/DAD at 1 ppm level[J].Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2004, 36(2):317-325.
[9] OZDEMIR Z, TRAS B, UNEY K.Distribution of hydrophilic and lipophilic antibacterial drugs in skim milk, cream, and casein[J].Journal of Dairy Science, 2018, 101(12):10 694-10 702.
[10] VINCENT U, GIZZI G, HOLST C, et al.Validation of an analytical method for the determination of spiramycin, virginiamycin and tylosin in feeding-stuffs by thin-layer chromatography and bio-autography[J].Food Additives and Contaminants, 2007, 24(4):351-359.
[11] PATYRA E, NEBOT C, GAVIL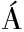 N R E, et al.Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of tiamulin, trimethoprim, tylosin, sulfadiazine and sulfamethazine in medicated feed[J].Food Additives & Contaminants:Part A, 2018, 35(5):882-891.
N R E, et al.Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of tiamulin, trimethoprim, tylosin, sulfadiazine and sulfamethazine in medicated feed[J].Food Additives & Contaminants:Part A, 2018, 35(5):882-891.
[12] JANK L, MARTINS M T, ARSAND J B, et al.High-throughput method for macrolides and lincosamides antibiotics residues analysis in milk and muscle using a simple liquid-liquid extraction technique and liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry analysis (LC-MS/MS)[J].Talanta, 2015, 144:686-695.
[13] HUANG J X, YAO C Y, YANG J Y, et al.Design of novel haptens and development of monoclonal antibody-based immunoassays for the simultaneous detection of tylosin and tilmicosin in milk and water samples[J].Biomolecules, 2019, 9(12):770.
[14] HENDRICKSON O D, ZVEREVA E A, ZHERDEV A V, et al.Development of a double immunochromatographic test system for simultaneous determination of lincomycin and tylosin antibiotics in foodstuffs[J].Food Chemistry, 2020, 318:126510.
[15] LE T, ZHU L Q, YANG X.A quantum dot-based immunoassay for screening of tylosin and tilmicosin in edible animal tissues[J].Food Additives & Contaminants:Part A, 2015, 32(5):719-724.
[16] CHEN W Y, HUANG Z, HU S, et al.Invited review:Advancements in lateral flow immunoassays for screening hazardous substances in milk and milk powder[J].Journal of Dairy Science, 2019, 102(3):1 887-1 900.
[17] SHI Q Q, HUANG J, SUN Y N, et al.Utilization of a lateral flow colloidal gold immunoassay strip based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for ultrasensitive detection of antibiotics in milk[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2018, 197:107-113.
[18] RYU J H, KWON M, MOON J D, et al.Development of a rapid automated fluorescent lateral flow immunoassay to detect hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), antibody to HBsAg, and antibody to hepatitis C[J].Annals of Laboratory Medicine, 2018, 38(6):578-584.
[19] MARTISKAINEN I, JUNTUNEN E, SALMINEN T, et al.Double-antigen lateral flow immunoassay for the detection of anti-HIV-1 and-2 antibodies using upconverting nanoparticle reporters[J].Sensors, 2021, 21(2):330.
[20] LI G, WANG A P, CHEN Y M, et al.Development of a colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic strip for rapid detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike protein[J].Frontiers in Immunology, 2021, 12:635677.
[21] LI C Z, VANDENBERG K, PRABHULKAR S, et al.Paper based point-of-care testing disc for multiplex whole cell bacteria analysis[J].Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2011, 26(11):4 342-4 348.
[22] ZHANG G P, GUO J Q, WANG X N, et al.Development and evaluation of an immunochromatographic strip for trichinellosis detection[J].Veterinary Parasitology, 2006, 137(3-4):286-293.
[23] VERHEIJEN R, STOUTEN P, CAZEMIER G, et al.Development of a one step strip test for the detection of sulfadimidine residues[J].The Analyst, 1998, 123(12):2 437-2 441.
[24] LI Z X, ZHAO F P, TANG T T, et al.Development of a colloidal gold immunochromatographic strip assay for rapid detection of bovine rotavirus[J].Viral Immunology, 2019, 32(9):393-401.
[25] NA G Q, HU X F, YANG J F, et al.A rapid colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic strip assay for monitoring nitroxynil in milk[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2020, 100(5):1 860-1 866.
[26] ZHANG Y Y, HE F Y, WAN Y P, et al.Generation of anti-trenbolone monoclonal antibody and establishment of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of trenbolone in animal tissues, feed and urine[J].Talanta,2011, 83(3):732-737.
[27] ZHANG G P, WANG X N, YANG J F, et al.Development of an immunochromatographic lateral flow test strip for detection of β-adrenergic agonist clenbuterol residues[J].Journal of Immunological Methods, 2006, 312(1-2):27-33.
[28] WANG Z X, GUO L L, LIU L Q, et al.Colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic strip assay for the rapid detection of three natural estrogens in milk[J].Food Chemistry, 2018, 259:122-129.
[29] 徐凤琴, 朱群艳, 张婳, 等.血清中可溶性白介素-2受体胶体金免疫层析试纸检测方法研究[J].分析化学, 2021, 49(6):973-981.
XU F Q, ZHU Q Y, ZHANG H, et al.Preparation of collidal gold-labeled immunochromatographic strips for detection method of soluble interleukin-2 receptors in real samples[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 49(6):973-981.
[30] TANG Q Y, ZHANG C X.Data Processing System (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research[J].Insect Science, 2013, 20(2):254-260.
[31] HU D F, FULTON B, HENDERSON K, et al.Identification of tylosin photoreaction products and comparison of ELISA and HPLC methods for their detection in water[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(8):2 982-2 987.
[32] GAUDIN V, HEDOU C, VERDON E.Validation of two ELISA kits for the screening of tylosin and streptomycin in honey according to the European decision 2002/657/EC[J].Food Additives & Contaminants:Part A, 2013, 30(1):93-109.