虹鳟(Oncorhynchus mykiss)为鲑科、太平洋鲑属的一种鲑鱼,该鱼适应生长于冷水环境中[1-3],其鱼肉富含氨基酸、蛋白质,脂肪酸等营养成分,因肉质鲜嫩,口感优良,风味独特,营养价值丰富,深受广大消费者的喜爱[4]。其中,氨基酸作为人体、动物所需营养成分及蛋白质的基本组成单元,是组成生命体的重要基础物质,其含量对人体和动物具有重要的生理意义。有研究报道指出,游离氨基酸含量可以判断肉类食品的滋味特征,是关联和影响肉类食品风味及品质的重要成分[5-9],可分为鲜味(门冬氨酸、谷氨酸)、甜味(苏氨酸、脯氨酸、丙氨酸、甘氨酸和丝氨酸)、苦味(苯丙氨酸、亮氨酸、异亮氨酸、甲硫氨酸、缬氨酸、赖氨酸、酪氨酸、组氨酸和精氨酸)三类[10],可作为肉类食品滋味特征评价的重要指标。因此,对虹鳟鱼肉中游离氨基酸含量测定有助于分析该食品的滋味特征。
目前,氨基酸测定有氨基酸自动分析仪-茚三酮显色法[11]、高效液相色谱-柱前衍生法[12-13]、高效液相色谱-荧光检测法[14]、高效液相色谱-质谱联用仪[15-16]等分析方法[17],多数方法需衍生化试剂处理,且衍生物不稳定,检测信号衰减快,干扰因素较多,影响检测。氨基酸分析仪虽具有灵敏度高、分辨率高和检测准确的优势,但仅应用于氨基酸分析,且衍生物不稳定。因此,本研究建立超高效液相色谱-质谱联用仪分析鱼肉游离氨基酸的方法,同时测定不同大小虹鳟鱼肉中的16种游离氨基酸含量,并结合化学计量学方法分析其含量与滋味特征的关系,以期为虹鳟品质评价及产品开发利用提供参考基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试剂与材料
氨基酸混合对照品溶液,日本Shimadzu公司[天冬氨酸(Asp,332.8 μg/mL)、谷氨酸(Glu,367.8 μg/mL)、丝氨酸(Ser,262.7 μg/mL)、组氨酸(His,387.9 μg/mL)、甘氨酸(Gly,187.7 μg/mL)、苏氨酸(Thr,297.8 μg/mL)、精氨酸(Arg,435.5 μg/mL)、丙氨酸(Ala,222.7 μg/mL)、酪氨酸(Tyr,453.0 μg/mL)、缬氨酸(Val,292.9 μg/mL)、甲硫氨酸(Met,373.0 μg/mL)、异亮氨酸(Ile,327.9 μg/mL)、苯丙氨酸(Phe,413.0 μg/mL)、赖氨酸(Lys,365.5 μg/mL)、亮氨酸(Leu,327.9 μg/mL)、脯氨酸(Pro,287.8 μg/mL)];乙腈和甲酸(均为色谱纯),美国Thermo Fisher公司;甲酸铵(色谱纯),上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;水为超纯水;其他试剂均为分析纯。
在青海虹鳟养殖场分别采集三倍体虹鳟幼鱼[LB;体重(0.14±0.01) kg]、中鱼[SY;体重(0.73±0.16) kg)、成鱼[BM;体重(3.97±0.47) kg]各12尾,剖取背部肌肉置于-80 ℃冰箱中待测。
1.2 仪器与设备
AB Sciex QTRAP 5500三重四极杆-线性离子阱质谱仪,美国AB Sciex公司;Exion LC AD超高效液相色谱仪,美国AB Sciex公司;ME204E电子分析天平,德国Sartorius公司;5418 R低温高速离心机,美国Eppendorf公司;LWFS31310水纯化系统仪,美国PALL公司;XHF-D高速内切式匀浆机,宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司。
1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 对照品溶液的配制
精密吸取适量16种氨基酸混合对照品溶液,置于10 mL棕色容量瓶中,用V(水)∶V(乙腈)=1∶3稀释并定容,得不同浓度梯度的对照品储备液,备用。
1.3.2 样品溶液的制备
参照CHENG等[18]和QI等[19]所述游离氨基酸含量测定方法,有所改动。精确称取虹鳟鱼背部肌肉约0.5 g,置于50 mL离心管中,加入约10 mL[V(水)∶V(乙腈)=1∶3]溶液定容至10 mL刻度,在4 ℃条件下,匀浆至混悬均匀,静置30 min,转移至2 mL离心管中,于13 000 r/min离心15 min;取上清液用0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤,制得待测样品液。
1.3.3 色谱条件
Acquity UPLC BEH Amide色谱柱(2.1 mm×100 mm,1.7 μm),柱温35 ℃,流速0.3 mL/min。流动相:5 mmol/L 甲酸铵-0.1%甲酸水溶液(A),5 mmol/L 甲酸铵-0.1%甲酸乙腈(B)。梯度洗脱程序:0~2 min,100% B;2~5 min,100% B~87% B;5~8 min,87% B~79% B;8~12 min,79% B;12~17 min,79% B~73% B;17~20 min,73% B~50% B;进样体积2 μL。
1.3.4 质谱条件
电喷雾正离子源(electrospray ionization,ESI+),多反应监测(multiple- reaction monitoring,MRM)模式采集;喷雾电压5.5 kV;离子源温度450 ℃;气帘气压强138 kPa;喷雾气(Gas1) 压强310.3 kPa;辅助加热气压强(Gas2)379.2 kPa;碰撞气为Medium。得该质谱条件下,16种氨基酸的定量检测离子对、去簇电压(declustering potential,DP)、碰撞能量(collision energy,CE)等参数(表1)。
表1 16 种氨基酸的质谱参数
Table 1 Mass spectrum parameters of MRM of 16 kinds of cucurbitacin standard

编号化合物保留时间/min离子对DP/VCE/eV1Phe7.02166.2→120.243142Thr7.03120.2→77.1120113Leu7.12132.0→86.140104Ile7.37132.0→86.140155Met7.66150.1→104.150106Val8.04118.1→72.145107Lys8.05147.1→118.9118168Tyr8.05182.2→136.245179Pro8.08116.1→70.0601010Asp8.67134.1→74.1401011Ala8.9990.1→44.0351012Gly9.4776.0→30.151613Ser10.02106.1→60.045814Glu10.06148.1→84.1501415His12.58156.1→110.1801616Arg12.93175.1→70.16018
1.4 数据处理
所得实验数据采用IBM SPSS Statistics 22 (SPSS Corp, Chicago, USA)处理并进行单因素方差分析,实验数据P<0.05具有统计学意义;多元统计分析采用SIMCA 14.1 (Umerics AB, Malmo, Sweden),进行无监督的主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA),采用MetaboAnalyst 5.0 (https://www.metaboanalyst.ca/)在线绘制聚类热图。
2 结果与分析
2.1 条件优化
分别使用ESI正、负离子源,MRM检测,发现氨基酸在正离子模式下信号响应度高,故选择该离子模式作为检测条件。另外,因亮氨酸和异亮氨酸属于同分异构体,分子质量及定量离子对相同,需在UPLC色谱中分离且根据保留行为区别,故分别考察了不同的洗脱溶剂,包括向流动相中加入0.1%(体积分数)甲酸或5 mmol/L甲酸铵,有机相选择甲醇、乙腈,流动相等度和梯度洗脱程序等因素;不同的色谱柱,包括Waters Acquity UPLC BEH C18,Waters Acquity UPLC BEH Amide,Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18等;最终以5 mmol/L甲酸铵水溶液(0.1%甲酸)-5 mmol/L甲酸铵乙腈(0.1%甲酸)作为流动相,Waters BEH Amide色谱柱,进行梯度洗脱时为最优分离条件(图1),因此选择该色谱-质谱条件进行后续分析。

图1 16 种氨基酸MRM图
Fig.1 MRM chromatograms of 16 amino acids
2.2 线性关系
精密移取预先配制的各不同浓度混合对照品溶液,按1.3.3项色谱条件和1.3.4项质谱条件测定,以峰面积为纵坐标(y),质量浓度为横坐标(x),得16种氨基酸线性回归方程(表2)。
表2 16种氨基酸的线性方程、相关系数及线性范围
Table 2 Regression equation, correlation and linear range of 16 amino acids
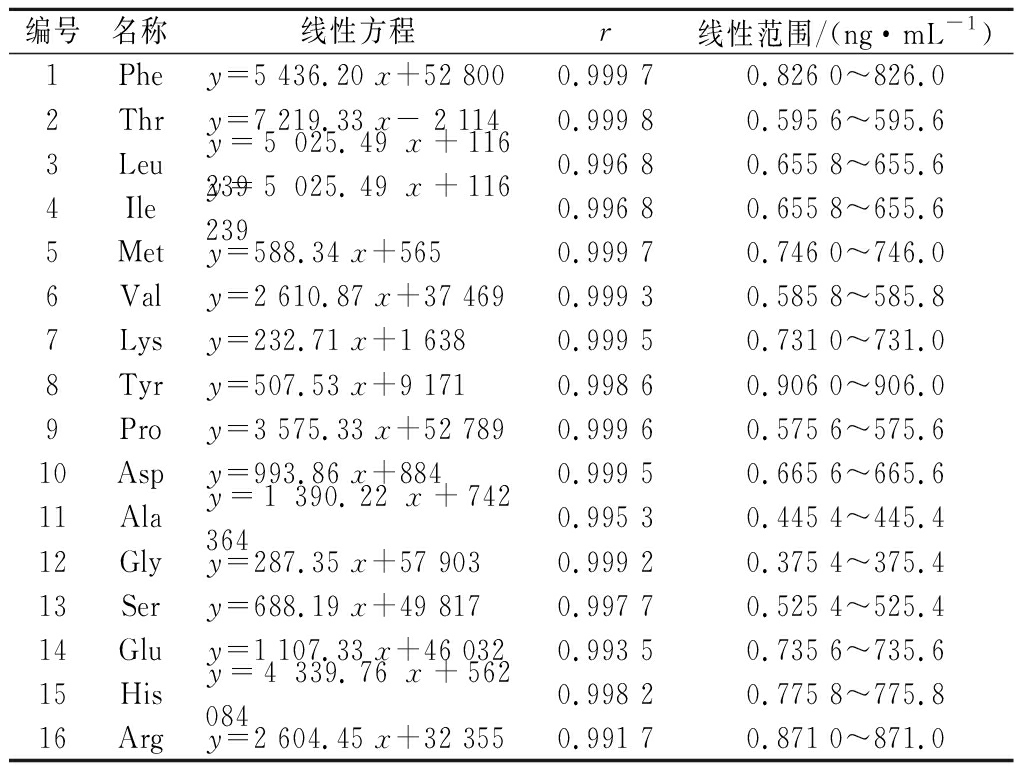
编号名称线性方程r线性范围/(ng·mL-1)1Phey=5 436.20 x+52 8000.999 70.826 0~826.02Thry=7 219.33 x- 2 1140.999 80.595 6~595.63Leuy=5 025.49 x+116 2390.996 80.655 8~655.64Iley=5 025.49 x+116 2390.996 80.655 8~655.65Mety=588.34 x+5650.999 70.746 0~746.06Valy=2 610.87 x+37 4690.999 30.585 8~585.87Lysy=232.71 x+1 6380.999 50.731 0~731.08Tyry=507.53 x+9 1710.998 60.906 0~906.09Proy=3 575.33 x+52 7890.999 60.575 6~575.610Aspy=993.86 x+8840.999 50.665 6~665.611Alay=1 390.22 x+742 3640.995 30.445 4~445.412Glyy=287.35 x+57 9030.999 20.375 4~375.413Sery=688.19 x+49 8170.997 70.525 4~525.414Gluy=1 107.33 x+46 0320.993 50.735 6~735.615Hisy=4 339.76 x+562 0840.998 20.775 8~775.816Argy=2 604.45 x+32 3550.991 70.871 0~871.0
2.3 精密度、重复性和稳定性
采用上述已优化的方法,并考察精密度、重复性和稳定性,按1.3.3项色谱条件和1.3.4项质谱条件测定,计算得出16种氨基酸保留时间的相对标准差(relative standard deviation,RSD)分别为0.03%~0.33%、0.05%~0.98% 和1.22%~3.48%;峰面积的RSD分别为1.16%~3.40%、1.72%~3.98%和2.54%~3.97%。表明此方法仪器精密度和重复性良好,供试样品溶液稳定。
2.4 加样回收率
精密称取已知含量的同一虹鳟鱼肉样品6份,精密加入适量16种氨基酸混合对照品溶液,按1.3.3项色谱条件和1.3.4项质谱条件测定,记录峰面积,计算回收率。16种氨基酸的平均加样回收率为98.38%~103.57%,RSD分别为0.34%~2.89%。
2.5 含量测定
按1.3.2项的样品处理方法及1.3.3项色谱条件和1.3.4项质谱条件,对36个不同大小虹鳟鱼肉样品中16种氨基酸的含量进行测定,并采用外标法计算。结果发现,不同大小虹鳟鱼肉样品中Met含量无显著差异(P>0.05),其他15种氨基酸的含量差异极显著(P<0.01);Gly、His、Ala和Glu四种氨基酸占总游离氨基酸的比例较高(表3)。
2.6 滋味相关性分析
虹鳟鱼肉中游离的氨基酸的含量及阈值对其风味影响具有重要作用,经查阅16种呈味氨基酸的阈值[20-21],并参照CHEN等[22]和SABIKUN等[23]所述的滋味活度值评价方法,氨基酸的滋味活度值大于1对样品的滋味有贡献,滋味活度值小于1贡献不显著,对虹鳟鱼肉进行呈味相关性分析;结果表明在幼鱼鱼肉中滋味活度值大于1的氨基酸为谷氨酸、精氨酸;在中鱼鱼肉中为甘氨酸、精氨酸;在成鱼鱼肉中为甲硫氨酸、精氨酸。总鲜味氨基酸活度贡献值大小依次为:中鱼、幼鱼、成鱼;总甜味氨基酸活度贡献值大小依次为:幼鱼、中鱼、成鱼;总苦味氨基酸活度贡献值大小依次为:成鱼、中鱼、幼鱼(表4)。因此,随着虹鳟鱼体型增长,该鱼肉滋味氨基酸具有差异并呈现动态变化。
表3 不同大小虹鳟鱼肉中游离氨基酸含量 单位:mg/100g
Table 3 Contents of free amino acids in muscle of rainbow trout with different body sizes
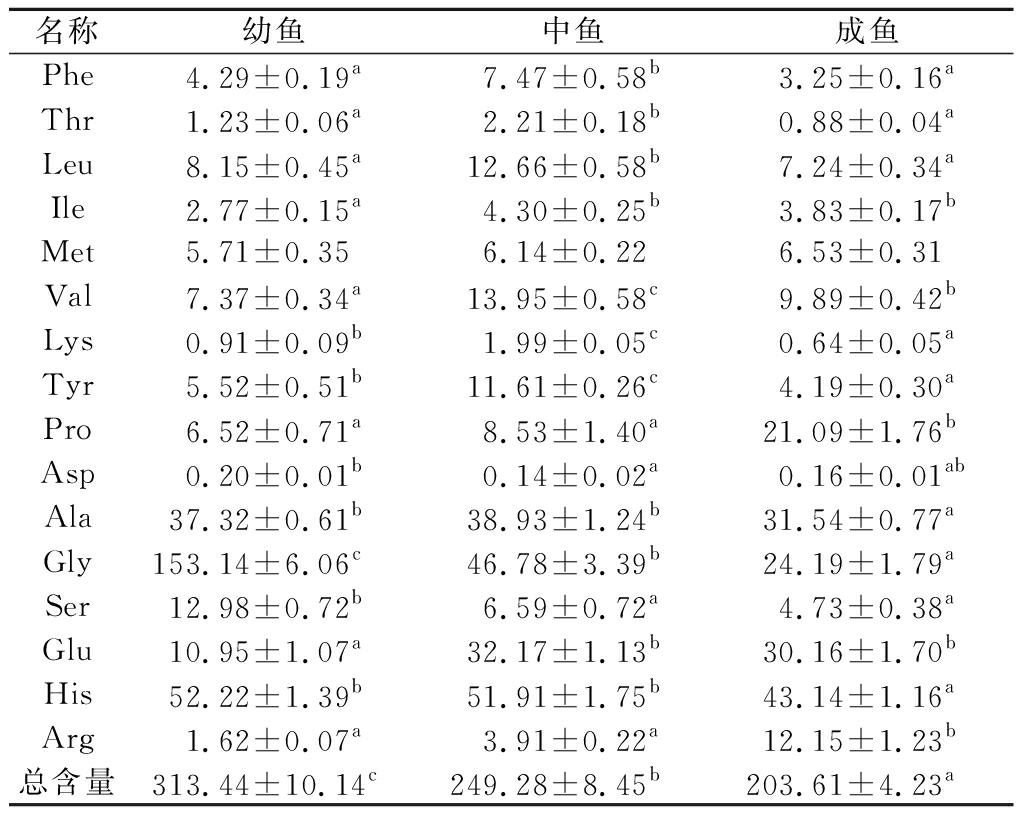
名称幼鱼中鱼成鱼Phe4.29±0.19a7.47±0.58b3.25±0.16aThr1.23±0.06a2.21±0.18b0.88±0.04aLeu8.15±0.45a12.66±0.58b7.24±0.34aIle2.77±0.15a4.30±0.25b3.83±0.17bMet5.71±0.356.14±0.226.53±0.31Val7.37±0.34a13.95±0.58c9.89±0.42bLys0.91±0.09b1.99±0.05c0.64±0.05aTyr5.52±0.51b11.61±0.26c4.19±0.30aPro6.52±0.71a8.53±1.40a21.09±1.76bAsp0.20±0.01b0.14±0.02a0.16±0.01abAla37.32±0.61b38.93±1.24b31.54±0.77aGly153.14±6.06c46.78±3.39b24.19±1.79aSer12.98±0.72b6.59±0.72a4.73±0.38aGlu10.95±1.07a32.17±1.13b30.16±1.70bHis52.22±1.39b51.91±1.75b43.14±1.16aArg1.62±0.07a3.91±0.22a12.15±1.23b总含量313.44±10.14c249.28±8.45b203.61±4.23a
注:同行上标字母相同表示无显著差异(P>0.05),不同表示显著差异(P<0.01)
表4 不同大小虹鳟鱼肉中游离氨基酸滋味活度值
Table 4 Taste activity values of free amino acids in muscle of rainbow trout with different body sizes
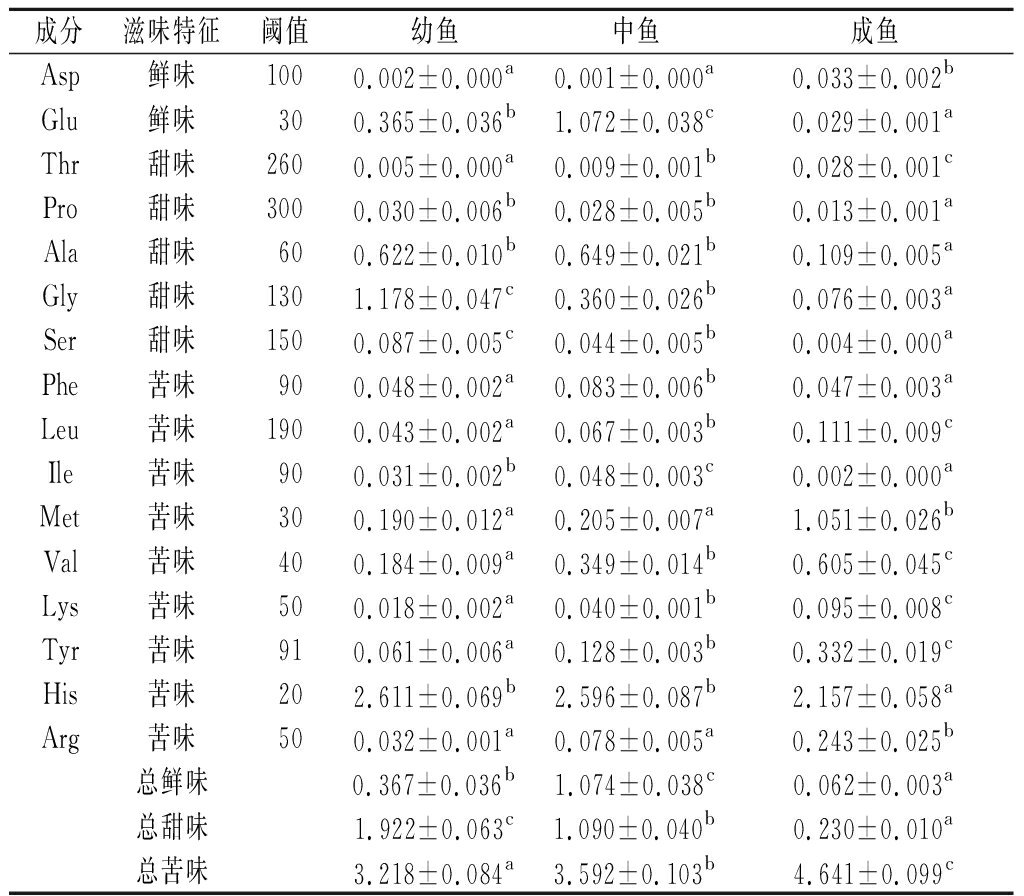
成分滋味特征阈值幼鱼中鱼成鱼Asp鲜味1000.002±0.000a0.001±0.000a0.033±0.002bGlu鲜味300.365±0.036b1.072±0.038c0.029±0.001aThr甜味2600.005±0.000a0.009±0.001b0.028±0.001cPro甜味3000.030±0.006b0.028±0.005b0.013±0.001aAla甜味600.622±0.010b0.649±0.021b0.109±0.005aGly甜味1301.178±0.047c0.360±0.026b0.076±0.003aSer甜味1500.087±0.005c0.044±0.005b0.004±0.000aPhe苦味900.048±0.002a0.083±0.006b0.047±0.003aLeu苦味1900.043±0.002a0.067±0.003b0.111±0.009cIle苦味900.031±0.002b0.048±0.003c0.002±0.000aMet苦味300.190±0.012a0.205±0.007a1.051±0.026bVal苦味400.184±0.009a0.349±0.014b0.605±0.045cLys苦味500.018±0.002a0.040±0.001b0.095±0.008cTyr苦味910.061±0.006a0.128±0.003b0.332±0.019cHis苦味202.611±0.069b2.596±0.087b2.157±0.058aArg苦味500.032±0.001a0.078±0.005a0.243±0.025b总鲜味0.367±0.036b1.074±0.038c0.062±0.003a总甜味1.922±0.063c1.090±0.040b0.230±0.010a总苦味3.218±0.084a3.592±0.103b4.641±0.099c
注:同行上标字母相同表示无显著差异(P>0.05),不同表示显著差异(P<0.01)
对不同规格虹鳟鱼肉16种氨基酸滋味活度值进行PCA分析(图2-a)和热图聚类分析(图3),结果三者呈现明显的分离效果,且主成分贡献值较高,有效地反映出各变量的信息,在滋味特征方面有明显不同。结合变量投影重要性指标(variable importance in projection,VIP)得分(图2-b)并选择VIP值>1的成分作为起主要作用的成分,Glu、Phe、Gly、Ile和Ser对区分不同规格鱼肉滋味起主要作用。

a-PCA;b-VIP得分图
图2 不同大小虹鳟鱼肉游离氨基酸滋味活度值 PCA及VIP得分图
Fig.2 Principal component analysis and VIP score plot for taste activity values of free amino acids in muscle of rainbow trout with different body sizes
3 结论
本研究采用超高效液相色谱-三重四级杆线性离子阱质谱联用仪测定不同大小虹鳟鱼肉中16种游离氨基酸含量,并结合化学计量学方法,对不同大小虹鳟鱼肉中各游离氨基酸滋味活度值进行PCA分析探讨各游离氨基酸含量对虹鳟鱼肉滋味贡献值,证明不同大小虹鳟鱼肉中各游离氨基酸含量不同,其滋味呈现不同特征。
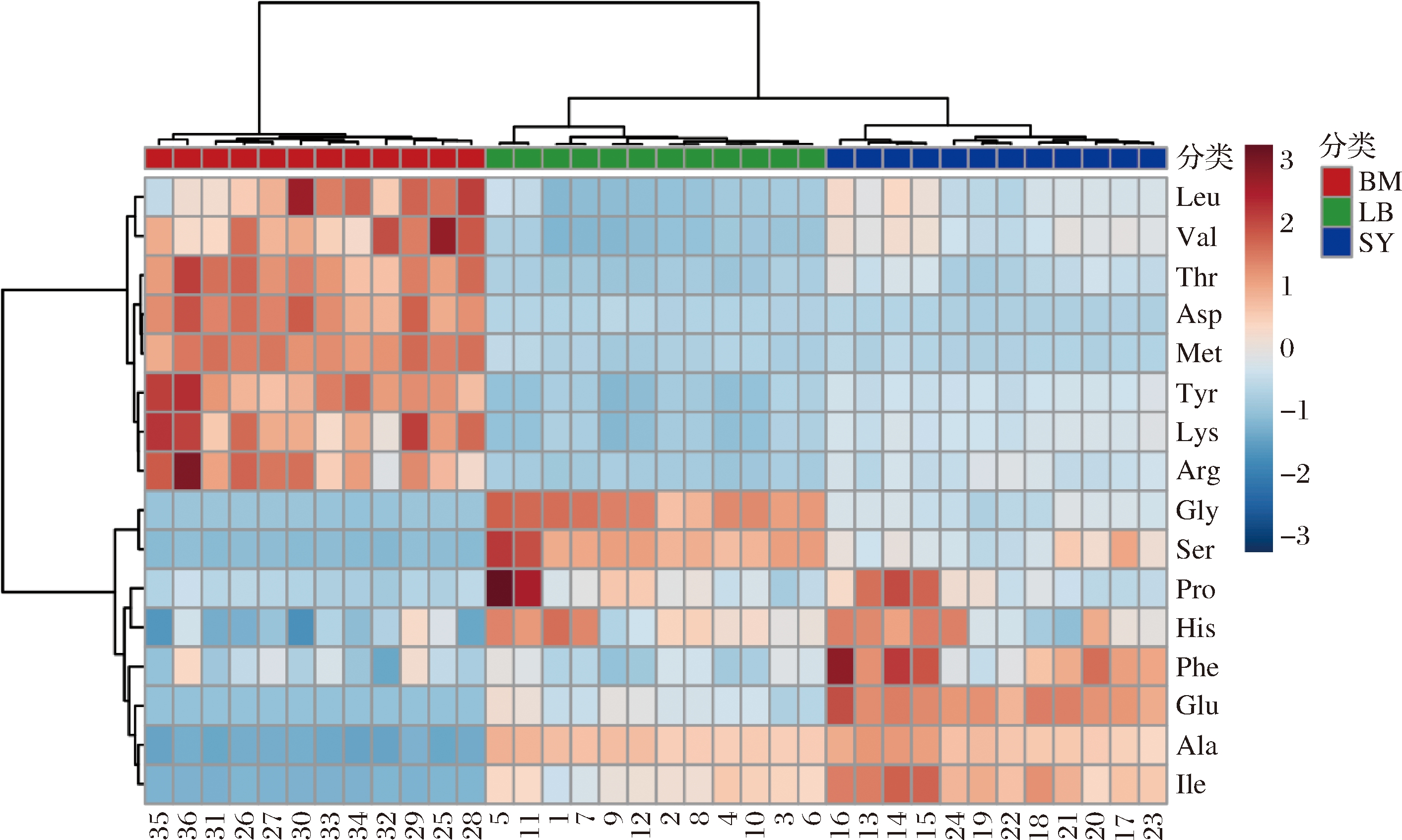
图3 不同大小虹鳟鱼肉游离氨基酸滋味活度值聚类热图
Fig.3 Clustering heat map for taste activity values of free amino acids in muscle of rainbow trout with different body sizes
[1] JIANG X Y, DONG S L, LIU R X, et al.Effects of temperature, dissolved oxygen, and their interaction on the growth performance and condition of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)[J].Journal of Thermal Biology, 2021, 98:102928.
[2] MENG Y Q, QIAN K K, MA R, et al.Effects of dietary lipid levels on sub-adult triploid rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss):1.Growth performance, digestive ability, health status and expression of growth-related genes[J].Aquaculture, 2019, 513:734394.
[3] SINGH A K, SRIVASTAVA S C.Improved feeding strategy to optimize growth and biomass for up-scaling rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum 1792) farming in Himalayan region[J].Aquaculture, 2021, 542:736851.
[4] 吴永俊. 虹鳟鱼肉风味影响因素研究及鱼骨新产品开发[D].喀什:喀什大学, 2020.
WU Y J.A Study on influencing factors of flavor substances of rainbow trout and development of new fish bone products[D].Kashi:Kashi University, 2020.
[5] LYU H B, MA Y Y, HU C T, et al.The individual and combined effects of hypoxia and high-fat diet feeding on nutrient composition and flesh quality in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)[J].Food Chemistry, 2021, 343:128479.
[6] 陈剑岚. 草鱼的生理差异及保藏温度对肌肉呈味成分的影响[D].上海:上海海洋大学, 2017.
CHEN J L.Effects of physiological differences and preservation temperature on taste components of grass carp meat[D].Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2017.
[7] CHENG X L, LI M F, LENG X J, et al.Creatine improves the flesh quality of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) reared in freshwater[J].Food Chemistry, 2021, 354:129498.
[8] JIA W, SHI Q Y, SHI L.Effect of irradiation treatment on the lipid composition and nutritional quality of goat meat[J].Food Chemistry, 2021, 351:129295.
[9] 卢佳芳, 朱煜康, 徐大伦, 等.不同剂量电子束辐照对花鲈鱼肉风味的影响[J].食品科学, 2021, 42(12):153-158.
LU J F, ZHU Y K, XU D L, et al.Effect of electron beam irradiation with different doses on flavor of Lateolabrax japonicus meat[J].Food Science, 2021, 42(12):153-158.
[10] 廖兰, 赵谋明, 崔春.肽与氨基酸对食品滋味贡献的研究进展[J].食品与发酵工业, 2009, 35(12):107-113.
LIAO L, ZHAO M M, CUI C.Review on the taste of peptides and amino acids to foodstuffs[J].Food and Fermentation Industries, 2009, 35(12):107-113.
[11] DAI W L, GU S Q, XU M J, et al.The effect of tea polyphenols on biogenic amines and free amino acids in bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) fillets during frozen storage[J].LWT, 2021, 150:111933.
[12] REIS G C L, GUIDI L R, FERNANDES C, et al.UPLC-UV method for the quantification of free amino acids, bioactive amines, and ammonia in fresh, cooked, and canned mushrooms[J].Food Analytical Methods, 2020, 13(8):1 613-1 626.
[13] 黄元河, 黄玉镯, 潘乔丹, 等.柱前衍生化 HPLC 法测定柊叶游离氨基酸成分及风味评价[J].食品工业科技, 2021, 42(1):292-296;303.
HUANG Y H, HUANG Y Z, PAN Q D, et al.Determination of free amino acid compositon in Phrynium rheedei by pre-column derivatization HPLC and flavor quality evaluation[J].Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(1):292-296;303.
[14] ![]() , et al.The distinct impact of multi-color LED light on nitrate, amino acid, soluble sugar and organic acid contents in red and green leaf lettuce cultivated in controlled environment[J].Food Chemistry, 2020, 310:125799.
, et al.The distinct impact of multi-color LED light on nitrate, amino acid, soluble sugar and organic acid contents in red and green leaf lettuce cultivated in controlled environment[J].Food Chemistry, 2020, 310:125799.
[15] RAIMBAULT A, NOIREAU A, WEST C.Analysis of free amino acids with unified chromatography-mass spectrometry-application to food supplements[J].Journal of Chromato Graphy A, 2020, 1 616:460772.
[16] QIU X, REYNOLDS R, JOHANNINGSMEIER S, et al.Determination of free amino acids in five commercial sweetpotato cultivars by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2020, 92:103522.
[17] VIOLI J P, BISHOP D P, PADULA M P, et al.Considerations for amino acid analysis by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry:A tutorial review[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 131:116018.
[18] CHENG X L, LI M F, LENG X J, et al.Creatine improves the flesh quality of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) reared in freshwater[J].Food Chemistry, 2021, 354:129498.
[19] QI J, ZHANG W W, XU Y, et al.Enhanced flavor strength of broth prepared from chicken following short-term frozen storage[J].Food Chemistry, 2021, 356:129678.
[20] 江津津, 严静, 郑玉玺, 等.不同产地传统鱼露风味特征差异分析[J].食品科学, 2021, 42(12):206-214.
JIANG J J, YAN J, ZHENG Y X, et al.Analysis of flavor characteristics of traditional fish sauce from different regions[J].Food Science, 2021, 42(12):206-214.
[21] 范婷婷, 赵晓燕, 李晓贝, 等.人工栽培和野生羊肚菌游离氨基酸主成分分析及综合评价[J].食品科学, 2022,43(6):295-302.
FAN T T, ZHAO X Y, LI X B, et al.Principal component analysis for comprehensive evaluation of free amino acids in cultivated and wild Morchella[J].Food Science, 2022,43(6):295-302.
[22] CHEN D W, ZHANG M.Non-volatile taste active compounds in the meat of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis)[J].Food Chemistry, 2007, 104(3):1 200-1 205.
[23] SABIKUN N, BAKHSH A, RAHMAN M S, et al.Volatile and nonvolatile taste compounds and their correlation with umami and flavor characteristics of chicken nuggets added with milkfat and potato mash[J].Food Chemistry, 2021, 343:128499.