神经退行性疾病,如阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer’s disease,AD)、帕金森病(Parkinson’s disease,PD)等是一组与衰老相关的神经系统异质性疾病,对人类健康和生活质量构成严重威胁[1-2]。近年来,研究表明来源于食药用菌的萜类、多糖、核苷、甾醇等代谢物质,能通过抗神经炎活性和神经保护活性预防和缓解神经退行性疾病[3]。
猴头菇[Hericium erinaceus(Bull.)Pers]又名猴头菌,猴头蘑、狮鬃菇、刺猬菌等,因其外观类似猴头而得名,在分类学上猴头菇隶属于担子菌门(Basidiomycota)、伞菌纲(Agariomycetes)、红菇目(Russulales)、猴头菌科(Hericiaceae)、猴头菌属(Hericium)。猴头菇是我国主要栽培的一种食药用菌,不仅味道鲜美,营养丰富,还富含萜类、多糖、活性蛋白、酮类、甾醇、生物碱、酚类等多种代谢产物,具有抗癌、抗菌、增强免疫力、抗炎、降血脂等生物活性[4-5]。鉴于其显著的益身特性,猴头菇被广泛用于药品、保健品以及膳食补充剂的重要原料,应用前景广阔[6-7]。在众多生理功能中,猴头菇在神经营养与神经保护方面的功效日益受到关注,已有研究在动物模型上观察到猴头菇在缓解阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病和与年龄相关的认知障碍方面的积极作用[8]。
猴头菌素(Erinacines)是一类鸟巢烷型(cyathanes)二萜化合物,是猴头菇中发挥神经营养与神经保护功能的关键活性成分。1994年,KAWAGISHI等[9]首次从猴头菇菌丝体中分离鉴定出含有鸟巢烷基本骨架和木糖基团的二萜化合物Erinacines A-C,并报道该类化合物能促进神经生长因子(nerve growth factor,NGF)合成后,猴头菌素的研究备受关注。后续研究表明猴头菌素可以有效穿过血脑屏障(blood-brain barrier,BBB),抑制神经炎症,具有促进神经突起生长和神经元营养的双重功能,有望开发为改善或预防人类神经系统疾病的先导化合物[10-12]。本文总结了猴头菌素的分离提取、生物合成与生理功能的研究进展,以期为猴头菌素的研发与利用提供参考,促进预防和缓解神经退行性疾病的膳食补充剂、功能性食品与新型药物的研发,同时促进猴头菇产业高值化发展。
1 猴头菌素分离与纯化
猴头菌素主要来源于猴头菇菌丝体,目前主要利用液态发酵与固态发酵培养菌丝后分离获得猴头菌素。由于猴头菌素自身不稳定性且不溶于水,大多利用甲醇、乙醇等有机溶剂进行提取,并通过石油醚、乙酸乙酯萃取,再利用硅胶柱层析、半制备高效液相色谱等方法进行分离纯化,目前已经分离或合成了27种猴头菌素(表1)。由于猴头菌素分离体系较为繁琐,不少研究者对其提取与纯化方法进行了优化。
表1 二十七种猴头菌素来源及其结构式
Table 1 Sources and structure of 27 Erinacines
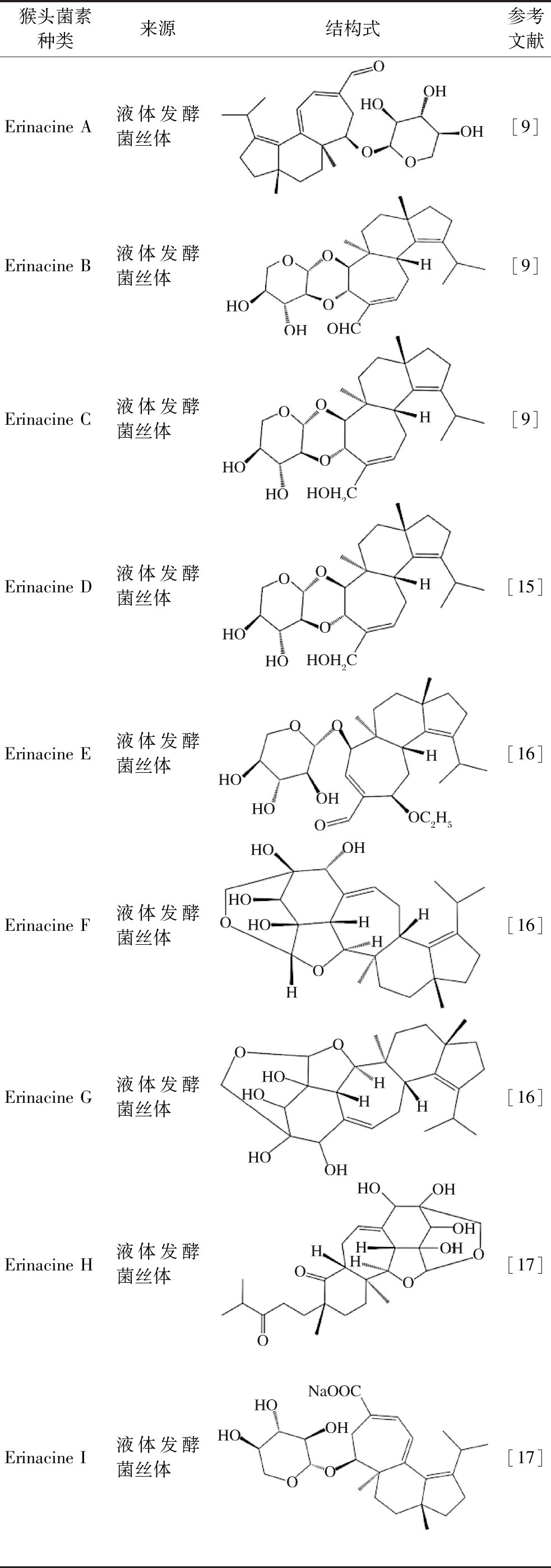
猴头菌素种类来源结构式参考文献Erinacine A液体发酵菌丝体[9]Erinacine B液体发酵菌丝体[9]Erinacine C液体发酵菌丝体[9]Erinacine D液体发酵菌丝体[15]Erinacine E液体发酵菌丝体[16]Erinacine F液体发酵菌丝体[16]Erinacine G液体发酵菌丝体[16]Erinacine H液体发酵菌丝体[17]Erinacine I液体发酵菌丝体[17]
续表1
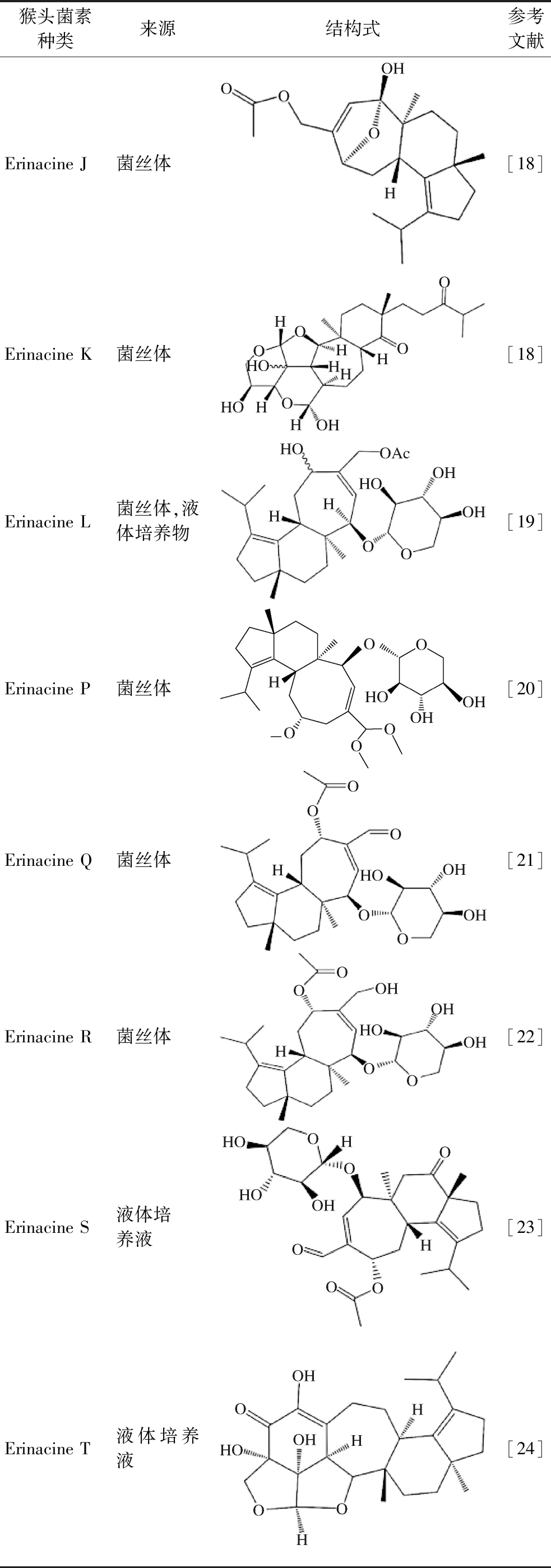
猴头菌素种类来源结构式参考文献Erinacine J菌丝体[18]Erinacine K菌丝体[18]Erinacine L菌丝体,液体培养物[19]Erinacine P菌丝体[20]Erinacine Q菌丝体[21]Erinacine R菌丝体[22]Erinacine S液体培养液[23]Erinacine T液体培养液[24]
续表1
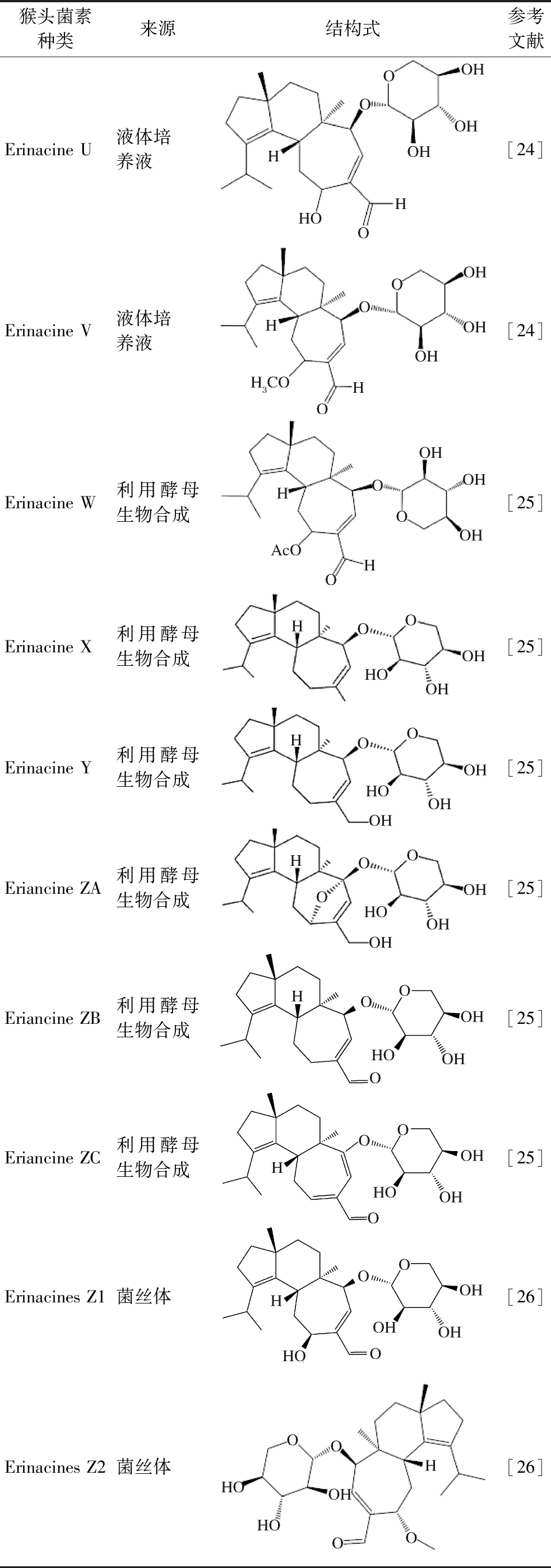
猴头菌素种类来源结构式参考文献Erinacine U液体培养液[24]Erinacine V液体培养液[24]Erinacine W利用酵母生物合成[25]Erinacine X利用酵母生物合成[25]Erinacine Y利用酵母生物合成[25]Eriancine ZA利用酵母生物合成[25]Eriancine ZB利用酵母生物合成[25]Eriancine ZC利用酵母生物合成[25]Erinacines Z1菌丝体[26]Erinacines Z2菌丝体[26]
VALU等[13]利用超声提取法从菌丝体中分离Erinacine A,并运用响应面法对提取工艺参数进行优化(如液料比、提取时间)。结果显示,当提取时间为45 min、液料比为20(mL∶g)时,Erinacine A提取率达到17.50%。此外,本团队利用高速逆流色谱法(high-speed countercurrent chromatography,HSCCC),采用正己烷/乙酸乙酯/甲醇/水(体积比4.5∶5∶4.5∶5)两相溶剂体系,分离出95%纯度的Erinacine A,并且发现不同菌株间Erinacine A的含量存在显著差异[14]。
Erinacines的本底含量低,因此通过优化猴头菇菌丝体的培养工艺来提升Erinacines的产量至关重要。液体发酵因具有生产周期短、效率高、产品质量稳定以及产物易分离等优点,广泛应用于猴头菌素的研究与生产。目前,研究主要集中于对Erinacine A与Erinacine C的工艺优化。KRZYCZKOWSKI等[27]采用单因素和中心复合旋转设计对猴头菇液体发酵培养基进行了优化。在10 L生物反应器中,使用葡萄糖69.87 g/L、酪蛋白胨11.17 g/L、NaCl 1.45 g/L、ZnSO4 55.24 mg/L、KH2PO4 1.0 g/L、pH为4.5的培养基发酵8 d后,Erinacine A的产量可达(192±42) mg/L。在液体发酵过程中,添加金属离子、微量元素等外源物质也是提升Erinacines产量的有效策略。CHANG等[28]在培养猴头菇时,额外添加了亚铁、铜、锰、镍等金属离子,使菌丝体生物量和Erinacine A产量分别达到16.8 g/L和(225±54) mg/L。WOLTERS等[29]采用燕麦片5 g/L,碳酸钙1.5 g/L,EDamin@K(一种水解乳清蛋白)0.5 g/L,pH为7.5的培养基,发酵6 d后Erinacine C产量可达2.73 g/L。此外,应用大规模生物反应器生产Erinacines亦有报道。LI等[30]利用20 t 发酵罐,培养基由酵母提取物2.5 g/L、葡萄糖45 g/L、大豆粉5 g/L、蛋白胨2.5 g/L和MgSO4 0.5 g/L组成,pH为4.5,发酵12 d后Erinacine A的产量可达5 mg/g菌丝体干重。
除液态发酵外,固态发酵培养基中添加无机物或微量元素进行发酵也有助于增加Erinacines含量。GERBEC等[31]在固态发酵培养基中添加不同浓度的微量元素,NaCl和酪蛋白质量分数为0.56%、3.4%时效果最好。CHENG等[32]发现在培养基中加入NaCl或ZnSO4可使Erinacine A的产率显著提高至120.97、165.36 mg/g。WOLTERS等[33]研究发现,利用酸化处理后的啤酒糟和小麦麸皮为培养基原料,Erinacine C含量分别为174.8、99.3 mg/g。
综上所述,培养基的组分和比例直接影响猴头菌素产量,添加适当的微量元素和激素等亦是增产的关键。然而,目前猴头菌素的分离纯化工作大多仍局限于实验室范畴,所采用的工艺仅能满足小规模的实验需求,未来需要对现有的培养、提取、分离纯化工艺进行放大和优化,以满足工业规模生产的需求,实现猴头菌素的大规模、稳定生产。
2 猴头菌素生物合成
以猴头菌素为代表的鸟巢烷型二萜是担子菌二萜类化合物中数量最多的类型之一[34-35]。大型真菌中主要是通过甲羟戊酸途径(mevalonate pathway,MVA)合成前体物质异戊烯基焦磷酸(isopentenyl diphosphate,IPP)和二甲基烯丙基焦磷酸(dimethylallyl diphosphate,DMAPP)。随后,前体物质经异戊烯转移酶(prenyltransferase)催化合成不同链长的异戊二烯单元,再经萜类合酶(terpenesynthases)催化发生脱磷、环化和羟化反应,形成结构各异的萜类化合物碳骨架。最后,这些萜类化合物骨架在各种修饰酶的作用下形成具有不同结构和功能的萜类化合物[36]。萜类化合物的下游代谢途径具种属特异性,包含多种不同的萜类合酶和修饰酶,从而决定了萜类化合物结构和功能的多样性。
随着真菌基因组迅速积累,极大促进了萜类化合物合成基因簇的鉴定。YANG等[37]在猴头菇基因组中鉴定了猴头菌素合成基因簇eri,该基因簇包含eriE[香叶基香叶基焦磷酸(geranylgeranylpyrophosphate,GGPP)合成酶]、eriG/F(UbiA型二萜环化酶)、eriA/C/I(P450酶)、eriJ(糖基转移酶)和eriB/H(短链脱氢酶),eriD(ABC转运蛋白)。其中,eriG是猴头菇中催化cyathane骨架环化的酶,属于UbiA异戊烯基转移酶超家族中的新成员。基因簇的鉴定为活性产物的生物合成与代谢调控研究提供了极大的便利。
近年来,为充分开发猴头菌素的应用潜力,研究者们对猴头菌素的生物合成途径进行了探索。LIU等[38]以米曲霉作为异源表达宿主,证明了eriA、C、H、I和J以及eriL对11-OH乙酰化的催化作用,并阐明了猴头菌素Q的生物合成路径(图1)。法尼基二磷酸(farnesyl diphosphate,FPP)经eriE催化形成GGPP,eriG将GGPP转化为化合物Cyatha-3,12-diene。在eriI的催化下,Cyatha-3,12-diene在七元环烯丙基C-14发生羟基化产生Erinacol。而后eriC催化Erinacol的七元环C-14羟基化产生Cyathadiol(4a)和化合物4b。在脱氢酶eriH或CPR(细胞色素P450还原酶)存在下eriA催化Cyathadiol(4a)的C-11羟基化产生化合物cyathatriol(5),而化合物4b的C-11发生羟基化产生化合物4c。乙酰转移酶eriL催化cyathatriol乙酰化合成11-O-乙酰鸟巢烷三醇[11-O-acetylcyathatriol(6)],eriH催化cyathatriol(5)和11-O-acetylcyathatriol(6)进一步氧化,分别产生Cyathin A3(7)和11-O-acetylcyathin A3(8)。糖基转移酶eriJ催化11-O-acetylcyathatriol(6)与糖基供体UDP-木糖发生糖基化反应产生猴头菌素Q;以UDP-D-葡萄糖为糖基供体的反应可产生猴头菌素Q2(12),猴头菌素Q2的侧链为葡萄糖基(C6H11O6)而不是木糖基(C5H9O5)。在没有eriL/eriJ的情况下,eriH将cyathatriol(5)转化为cyathin A3(7),而在eriL/eriJ/eriH存在的情况下cyathatriol(5)通过11-O-乙酰鸟巢烷三醇(6)迅速转化为Erinacine Q。
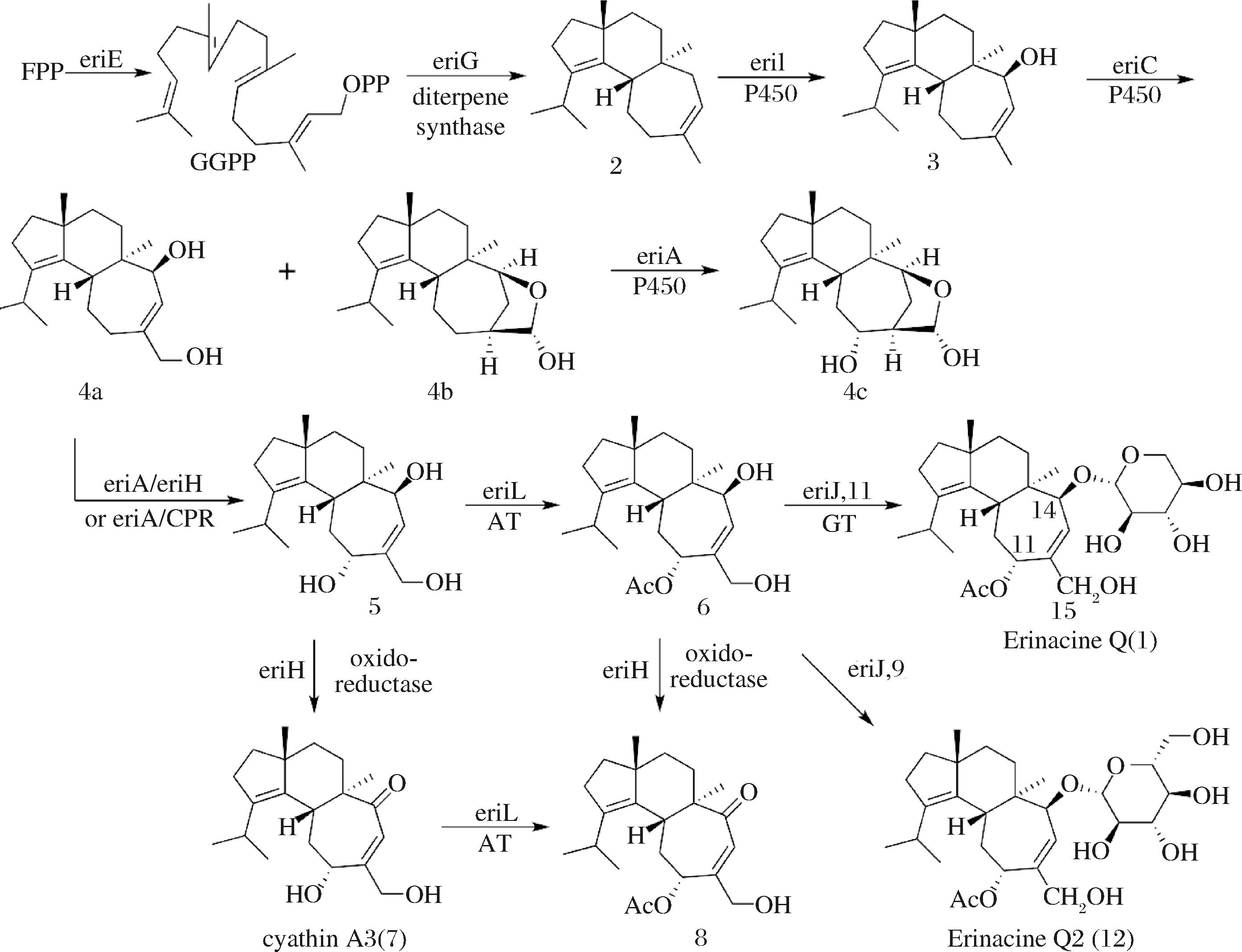
图1 猴头菌素Q的生物合成途径[38]
Fig.1 Biosynthesis pathway of Erinacine Q[38]
2021年,刘宏伟团队进一步发现并阐明了3个簇外基因(eriM、eriO和eriP)的功能,揭示了由FAD依赖的氧化酶eriM催化形成烯丙醛的过程,烯丙醛的形成触发串联迈克尔加成-消除反应进而形成了具有生物活性的Erinacine A;此外,他们在酿酒酵母中重新构筑鸟巢烷二萜的合成通路,实现了22个不同结构鸟巢烷二萜的生物合成,产率可达13.4~112.1 mg/L[25]。
尽管猴头菌素的生物合成研究已取得一定进展,但对其含量累积的代谢调控机制知之甚少。猴头菌素的积累涉及复杂的基因网络调控,其含量差异与相关基因的表达水平密切相关,已鉴定的基因如何调控猴头菌素含量尚不明确,其他重要的调控基因也有待进一步挖掘。转录因子可同时参与萜类合成基因簇中多个关键基因的表达调控[39],因此,鉴定关键转录因子是猴头菌素代谢调控研究的重点。深入解析猴头菌素基因调控网络,揭示其遗传基础,对于猴头菌素性状的遗传改良至关重要。
3 生理功效
神经退行性疾病与神经元的退化和死亡有关,导致神经通信和脑功能受损,其特征是认知、运动和自主神经功能逐渐下降[2]。近年来,人们对Erinacines在治疗神经疾病和认知障碍方面的潜在应用越来越关注。到目前为止,已经分离出了20余种不同的Erinacines,其中有10种具有神经营养活性,包括刺激NGF合成(Erinacines A、B、C、E、F和H)和促进神经突起生长(Erinacines T、U、V和P)。此外,已有大量文献通过体外、体内以及临床实验,报道了Erinacines的生物活性(表2)。
表2 Erinacine A的生理活性及其机制
Table 2 Physiological activity and mechanism of Erinacine A

3.1 神经营养作用
神经营养因子,例如神经生长因子NGF和脑源性神经营养因子(brain-derived neuotrophyic factor,BDNF)通过与Trk A/B受体(具有酪氨酸激酶活性的跨膜蛋白)和p75受体(一种富含半胱氨酸的糖蛋白)相互结合发挥其靶源性营养作用,在神经系统神经元的生长、维持和修复中起关键作用[49]。然而神经营养因子是蛋白质,分子量太大而无法通过血脑屏障,并且容易被代谢。因此寻找具有神经营养特性的小分子,增强内源性神经营养因子对预防和治疗神经退行性疾病非常关键。研究表明猴头菌素能能够刺激κ-opioid受体,有效穿过血脑屏障,促进神经营养因子的合成。KAWAGISHI等[9, 15]研究表明,添加1 mmol/L的Erinacines A-F,大鼠星形胶质细胞分泌的NGF分别为(250.1±36.2)、(129.7±6.5)、(299.1±59.6)、(141.5±18.2)、(105.0±5.2)、(175.0±52.0) pg/mL,显著高于肾上腺素(1.0 mmol/L时为69.2 pg/mL)。其他猴头菌素对NGF合成亦表现出促进作用,例如存在Erinacine H情况下,星形胶质细胞的NGF合成增加4倍[17],Erinacine Z1也增加了NGF的表达[26]。此外,RUPCIC等[26]研究表明还发现Erinacine C能增加NGF和BDNF的表达。SHIMBO等[42]测试了Erinacine A对大鼠不同脑区的影响,其结果表明由于Erinacine A刺激去甲肾上腺素合成,导致NGF分泌增加,也可能由于增加了神经营养蛋白3(NT-3)的水平,从而增强了去甲肾上腺素能神经元和去甲肾上腺素合成,去甲肾上腺素刺激NGF合成。
除了促进神经营养因子的合成,亦有研究表明猴头菌素通过促进神经营养因子的活性来促进神经突生长。ZHANG等[50]报道在NGF存在的情况下,Erinacines A没有促进大鼠嗜铬细胞瘤细胞PC-12中的NGF合成,但增强了Trk A和Erk1/2介导的NGF诱导神经突生长活性。后续的研究亦表明其他猴头菌素(例如Erinacines T-V)在NGF存在的情况下,对PC12细胞神经突生长与分化具有显著的促进作用[24]。LI等[41]于大鼠模型证实Erinacine A以能够诱导大鼠皮层神经元原代培养的神经突生长。Erinacine S能通过刺激神经类固醇的积累,显著增加小鼠和大鼠中枢神经系统(central nervous system,CNS)和外周神经系统(peripheral nervous system,PNS)神经元的神经突生长,并防止神经元凋亡[51]。
3.2 神经保护作用
众多研究表明,猴头菌还能通过调节细胞凋亡、减少氧化应激,抑制炎症等途径实现神经保护作用。Erinacines可激活抗凋亡信号通路如AKT和ERK,从而保护神经元免受凋亡,维持神经元的健康状态。LEE等[11]在体外N2a细胞实验中表明Erinacine A可以通过PAK1、AKT、LIMK2、MEK和ERK的磷酸化激活神经元存活通路,以及降低细胞死亡通路(TRAF2、ASK1、GADD45和p21),从而降低1-甲基-4-苯基-1,2,3,6-四氢吡啶(1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine,MPTP)诱导的神经毒性;此外在C57BL/6小鼠模型中,Erinacine A可以增加MPTP模型中多巴胺能神经元的蛋白酪氨酸羟化酶的表达,亦证实了Erinacine A在改善帕金森病和阿尔茨海默病的病理状况和行为缺陷方面的神经保护和治疗作用。此外,Erinacines可减轻与神经毒性和神经元凋亡相关的内质网应激反应,其主要作用机制涉及激活RE1α/TRAF2、JNK1/2和p38 MAPK通路,从而调控CHOP、IKB-β、NF-κB、Fas和Bax等多种因子,这些因素可以影响细胞凋亡过程,对神经元细胞起到保护作用[49]。
抗氧化应激在预防和减轻神经退行性疾病中发挥重要作用,研究表明猴头菌素可通过其抗氧化作用对脑氧化损伤起到保护作用。LEE等[45]研究表明给小鼠摄入富含Erinacine A的菌丝体后,小鼠脑内诱导型一氧化氮合成酶(inducible NO synthase,iNOS)表达降低,其保护作用可能是氧化应激和炎症状态降低的结果。LEE等[52]研究表明在轻度创伤性脑损伤(mild traumatic brain injury,mTBI)模型中,Erinacine C显著增加了抗氧化酶的蛋白表达水平,如过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)、硫氧还蛋白还原酶(thioredoxin reductase,TrxR)和超氧化物歧化酶1(铜锌型)[superoxide dismutase 1(Cu-Zn),SOD1],从而减少氧化应激。
Erinacines还可显著抑制炎症因子释放,减少炎症对神经元的损伤,维持神经元的健康。TSAI等[46]以15月龄高脂高糖饲料喂养的小鼠为实验对象,发现猴头菇菌丝体和Erinacine A通过降低小鼠海马组织中TNF-α和IL-1β mRNA的表达而发挥抗炎作用。
CHEN等[23]对APPswe/PS1 dE9小鼠进行了体内实验,以评估Erinacine A对AD的影响。其研究发现,口服猴头菇菌丝体30 d后,胰岛素降解酶(insulin-degrading enzyme,IDE)表达增强,大脑中β-淀粉样蛋白(amyloid β-protein,Aβ)的数量减少,降低其对神经元的毒性。此外,补充猴头菌素81 d后,转基因小鼠受损的大脑区域得到改善,导致行为缺陷逆转[10]。
3.3 改善认知作用
除神经营养与神经保护作用外,猴头菌素在改善认知障碍方面的潜力也得到广泛关注。MORI等[53]调查了经诊断患有轻度认知障碍的50至80岁日本男性和女性口服猴头菌的疗效,受试者每天服用3次,每次4片,持续16周,认知功能有所改善。![]() 等[54]双盲实验结果也表明补充Erinacine A可显著改善认知功能,还有研究表明长期摄入富含Erinacine A的菌丝体能够显著改善学习和记忆[45]。此外,LI等[48]证实了Erinacine A对缓解轻度阿尔茨海默病患者神经退行性疾病的有效性,每天口服含有5 mg/g的Erinacine A认知能力有所改善。猴头菌还可以增强刺激Akt/PKB信号通路的IDE表达水平或活性,减少tau蛋白的过度磷酸化从而缓解阿尔茨海默病,改善认知障碍[55]。
等[54]双盲实验结果也表明补充Erinacine A可显著改善认知功能,还有研究表明长期摄入富含Erinacine A的菌丝体能够显著改善学习和记忆[45]。此外,LI等[48]证实了Erinacine A对缓解轻度阿尔茨海默病患者神经退行性疾病的有效性,每天口服含有5 mg/g的Erinacine A认知能力有所改善。猴头菌还可以增强刺激Akt/PKB信号通路的IDE表达水平或活性,减少tau蛋白的过度磷酸化从而缓解阿尔茨海默病,改善认知障碍[55]。
3.4 抗癌作用
Erinacine A表现出抑制、调节与各种癌症进展有关的关键肿瘤通路,包括诱导细胞凋亡、阻止细胞周期和触发氧化还原应激[56]。Erinacine A能够产生活性氧和激活p70S6K和p21诱导抑制DLD-1结直肠癌细胞生长[44],还可抑制胃癌细胞(包括MKN28和TSGH 9201细胞)的活力和侵袭性[57]。
4 前景与展望
Erinacines具有显著的神经营养活性,能够刺激神经生长因子合成,对神经系统退行性疾病有潜在的治疗效果,然而其研发与应用也面临一些挑战。
首先,Erinacines现有的培养、提取、纯化或合成方法难以在工业生产中实现,尚处于实验室结构鉴定和活性验证阶段,其标准化和规模化生产仍是一个挑战,需建立严格的质量控制标准和检测方法。同时,市面上尚无Erinacines的标准品,缺少Erinacines标准品也是制约其发展的一大难题,关于Erinacines分离制备的方法尚需进一步优化,以提高效率和纯度。
其次,进一步选育高含量菌株也至关重要,对现有菌株进行筛选或者利用育种技术选育出含量高且稳定的菌株也是促进Erinacines开发利用的一个手段;还可以通过挖掘筛选与其合成相关基因,优化猴头菇发酵方法,提高Erinacines的纯度和产量,推动Erinacines的规模化应用。另外,由于Erinacines之间可以相互转化与生物合成,Erinacines之间相互转化内在的机制也值得探讨,促进Erinacines生物合成也是一个很有潜力的研究方向。
最后,基于Erinacines在神经保护和神经营养方面的显著效果,Erinacines可通过促进神经细胞的再生和修复,有助于恢复受损的神经功能,提高患者的生活质量,未来有望用于治疗阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病等神经退行性疾病。除此之外,Erinacines在抗癌治疗、镇痛镇静等方面也展现出潜力。然而,目前与Erinacines相关研究大多停留在细胞或动物水平,很少进行临床前或临床研究,缺乏大规模的临床研究来验证其安全性和有效性。目前对Erinacines在神经再生、保护中的具体作用机制尚不完全清楚。这些问题制约了Erinacines从实验室向市场的转移,未来将进一步深入研究Erinacines在神经再生、神经保护、抗癌等方面的具体作用机制,为其在临床上的应用提供理论依据。
Erinacines作为一种具有多种药理作用的天然化合物,其研究现状和未来发展均呈现出良好的态势。未来的研究和开发需要集中在选育高含量菌株、提高提取分离技术、阐明药理机制、开展临床研究、解决标准化和规模化生产以及开发出具有保健功能的功能性食品等问题上,有望以Erinacines为基础开发出新型药物、功能性食品等,为相关疾病的治疗提供更多选择,以促进猴头菇高值化发展。
[1] JABIR N R, FIROZ C K, BAEESA S S, et al.Synopsis on the linkage of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease with chronic diseases[J].CNS Neuroscience &Therapeutics, 2015, 21(1):1-7.
[2] DUGGER B N, DICKSON D W.Pathology of neurodegenerative diseases[J].Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2017, 9(7):a028035.
[3] LI N, LI H B, LIU Z B, et al.Unveiling the therapeutic potentials of mushroom bioactive compounds in Alzheimer’s disease[J].Foods, 2023, 12(15):2972.
[4] KOSTANDA E, MUSA S, PEREMAN I.Unveiling the chemical composition and biofunctionality of Hericium spp.fungi:A comprehensive overview[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, 25(11):5949.
[5] QIU Y, LIN G L, LIU W M, et al.Bioactive compounds in Hericium erinaceus and their biological properties:A review[J].Food Science and Human Wellness, 2024, 13(4):1825-1844.
[6] NIU B, ZHANG L, CHEN B D, et al.Extraction, purification, structural characteristics, biological activities, modifications, and applications from Hericium erinaceus polysaccharides:A review[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2025, 291:138932.
[7] RODA E, PRIORI E C, RATTO D, et al.Neuroprotective metabolites of Hericium erinaceus promote neuro-healthy aging[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(12):6379.
[8] BAILLY C, GAO J M.Erinacine A and related cyathane diterpenoids:Molecular diversity and mechanisms underlying their neuroprotection and anticancer activities[J].Pharmacological Research, 2020, 159:104953.
[9] KAWAGISHI H, SHIMADA A, SHIRAI R, et al.Erinacines A, B and C, strong stimulators of nerve growth factor (NGF)-synthesis, from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum[J].Tetrahedron letters, 1994, 35(10):1569-1572.
[10] TZENG T T, CHEN C C, CHEN C C, et al.The cyanthin diterpenoid and sesterterpene constituents of Hericium erinaceus Mycelium ameliorate Alzheimer’s disease-related pathologies in APP/PS1 transgenic mice[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(2):598.
[11] LEE K F, TUNG S Y, TENG C C, et al.Post-treatment with erinacine A, a derived diterpenoid of H.Erinaceus, attenuates neurotoxicity in MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease[J].Antioxidants, 2020, 9(2):137.
[12] BRANDALISE F, RODA E, RATTO D, et al.Hericium erinaceus in neurodegenerative diseases:From bench to bedside and beyond, how far from the shoreline?[J].Journal of Fungi, 2023, 9(5):551.
[13] VALU M V, SOARE L C, SUTAN N A, et al.Optimization of ultrasonic extraction to obtain erinacine A and polyphenols with antioxidant activity from the fungal biomass of Hericium erinaceus[J].Foods, 2020, 9(12):1889.
[14] LIU M C, LIU L L, SONG X Y, et al.Isolation and evaluation of erinacine A contents in mycelia of Hericium erinaceus strains[J].Foods, 2024, 13(11):1649.
[15] KAWAGISHI H, SIMADA A, SHIZUKI K, et al.Erinacine D, a stimulator of NGF-synthesis, from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum[J].Heterocyclic Communications, 1996, 2(1):51-54.
[16] KAWAGISHI H, SHIMADA A, HOSOKAWA S, et al.Erinacines E, F, and G, stimulators of nerve growth factor (NGF)-synthesis, from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum[J].Tetrahedron letters, 1996, 37(41):7399-7402.
[17] LEE E W, SHIZUKI K, HOSOKAWA S, et al.Two novel diterpenoids, erinacines H and I from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum[J].Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2000, 64(11):2402-2405.
[18] KAWAGISHI H, MASUI A, TOKUYAMA S, et al.Erinacines J and K from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum[J].Tetrahedron, 2006, 62(36):8463-8466.
[19] WEI J, LI J Y, FENG X L, et al.Unprecedented neoverrucosane and cyathane diterpenoids with anti-neuroinflammatory activity from cultures of the culinary-medicinal mushroom Hericium erinaceus[J].Molecules, 2023, 28(17):6380.
[20] KENMOKU H, SASSA T, KATO N.Isolation of erinacine P, a new parental metabolite of cyathane-xylosides, from Hericium erinaceum and its biomimetic conversion into erinacines A and B[J].Tetrahedron Letters, 2000, 41(22):4389-4393.
[21] KENMOKU H, SHIMAI T, TOYOMASU T, et al.Erinacine Q, a new erinacine from Hericium erinaceum, and its biosynthetic route to erinacine C in the basidiomycete[J].Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2002, 66(3):571-575.
[22] MA B J, ZHOU Y, LI L Z, et al.A new cyathane-xyloside from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum[J].Zeitschrift Für Naturforschung B, 2008, 63(10):1241-1242.
[23] CHEN C C, TZENG T T, CHEN C C, et al.Erinacine S, a rare sesterterpene from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceus[J].Journal of Natural Products, 2016, 79(2):438-441.
[24] ZHANG Y T, LIU L, BAO L, et al.Three new cyathane diterpenes with neurotrophic activity from the liquid cultures of Hericium erinaceus[J].The Journal of Antibiotics, 2018, 71(9):818-821.
[25] MA K, ZHANG Y T, GUO C, et al.Reconstitution of biosynthetic pathway for mushroom-derived cyathane diterpenes in yeast and generation of new “non-natural” analogues[J].Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2021, 11(9):2945-2956.
[26] RUPCIC Z, RASCHER M, KANAKI S, et al.Two new cyathane diterpenoids from mycelial cultures of the medicinal mushroom Hericium erinaceus and the rare species, Hericium flagellum[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(3):740.
[27] KRZYCZKOWSKI W, MALINOWSKA E, HEROLD F.Erinacine A biosynthesis in submerged cultivation of Hericium erinaceum:Quantification and improved cultivation[J].Engineering in Life Sciences, 2010, 10(5):446-457.
[28] CHANG C H, CHEN Y, YEW X X, et al.Improvement of erinacine A productivity in Hericium erinaceus mycelia and its neuroprotective bioactivity against the glutamate-insulted apoptosis[J].LWT-food Science and Technology, 2016, 65:1100-1108.
[29] WOLTERS N, SCHEMBECKER G, MERZ J.Erinacine C:A novel approach to produce the secondary metabolite by submerged cultivation of Hericium erinaceus[J].Fungal Biology, 2015, 119(12):1334-1344.
[30] LI I C, CHEN Y L, LEE L Y, et al.Evaluation of the toxicological safety of erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus in a 28-day oral feeding study in Sprague-Dawley rats[J].Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2014, 70:61-67.
[31] GERBEC B, ![]() E, GREGORI A, et al.Solid state cultivation of Hericium erinaceus biomass and erinacine:A production[J].Journal of Bioprocessing &Biotechniques, 2015, 5(3):1-5.
E, GREGORI A, et al.Solid state cultivation of Hericium erinaceus biomass and erinacine:A production[J].Journal of Bioprocessing &Biotechniques, 2015, 5(3):1-5.
[32] CHENG P Y, LIAO H Y, KUO C H, et al.Enhanced erinacine A production by Hericium erinaceus using solid-state cultivation[J].Fermentation, 2021, 7(3):182.
[33] WOLTERS N, SCHABRONATH C, SCHEMBECKER G, et al.Efficient conversion of pretreated brewer’s spent grain and wheat bran by submerged cultivation of Hericium erinaceus[J].Bioresource Technology, 2016, 222:123-129.
[34] ZHANG F L, FENG T.Diterpenes specially produced by fungi:Structures, biological activities, and biosynthesis (2010-2020)[J].Journal of Fungi, 2022, 8(3):244.
[35] 周一鸣, 祁建钊, 段应策, 等.大型担子菌中二萜化合物生物合成研究进展[J].菌物学报, 2023, 42(1):101-117.ZHOU Y M, QI J Z, DUAN Y C, et al.Research progress of the biosynthesis of diterpenoids in macro-basidiomycetes[J].Mycosystema, 2023, 42(1):101-117.
[36] XIAO H, ZHONG J J.Production of useful terpenoids by higher-fungus cell factory and synthetic biology approaches[J].Trends in Biotechnology, 2016, 34(3):242-255.
[37] YANG Y L, ZHANG S S, MA K, et al.Discovery and characterization of a new family of diterpene cyclases in bacteria and fungi[J].Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(17):4749-4752.
[38] LIU C W, MINAMI A, OZAKI T, et al.Efficient reconstitution of basidiomycota diterpene erinacine gene cluster in ascomycota host Aspergillus oryzae based on genomic DNA sequences[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(39):15519-15523.
[39] WANG Q, REDDY V A, PANICKER D, et al.Metabolic engineering of terpene biosynthesis in plants using a trichome-specific transcription factor Ms YABBY 5 from spearmint (Mentha spicata)[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14(7):1619-1632.
[40] WU Y L, CHEN S C, CHANG J C, et al.The protective effect of erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus Mycelium ethanol extract on oxidative Stress-Induced neurotoxicity in cell and Drosophila models of spinocerebellar Ataxia type 3[J].Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2023, 195:1-12.
[41] LI I C, CHEN W P, CHEN Y P, et al.Acute and developmental toxicity assessment of erincine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus mycelia in Sprague-Dawley rats[J].Drug and Chemical Toxicology, 2018, 41(4):459-464.
[42] SHIMBO M, KAWAGISHI H, YOKOGOSHI H.Erinacine A increases catecholamine and nerve growth factor content in the central nervous system of rats[J].Nutrition Research, 2005, 25(6):617-623.
[43] LEE K F, CHEN J H, TENG C C, et al.Protective effects of Hericium erinaceus Mycelium and its isolated erinacine A against ischemia-injury-induced neuronal cell death via the inhibition of iNOS/p38 MAPK and nitrotyrosine[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2014, 15(9):15073-15089.
[44] LU C C, HUANG W S, LEE K F, et al.Inhibitory effect of Erinacines A on the growth of DLD-1 colorectal cancer cells is induced by generation of reactive oxygen species and activation of p70S6K and p21[J].Journal of Functional Foods, 2016, 21:474-484.
[45] LEE L Y, CHOU W, CHEN W P, et al.Erinacine a-enriched Hericium erinaceus Mycelium delays progression of age-related cognitive decline in senescence accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8) mice[J].Nutrients, 2021, 13(10):3659.
[46] TSAI Y C, LIN Y C, HUANG C C, et al.Hericium erinaceus Mycelium and its isolated compound, erinacine A, ameliorate high-fat high-sucrose diet-induced metabolic dysfunction and spatial learning deficits in aging mice[J].Journal of Medicinal Food, 2019, 22(5):469-478.
[47] TSAI-TENG T, CHIN-CHU C, LEE L Y, et al.Erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus Mycelium ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease-related pathologies in APPswe/PS1 dE9 transgenic mice[J].Journal of Biomedical Science, 2016, 23(1):49.
[48] LI I C, CHANG H H, LIN C-H, et al.Prevention of early Alzheimer’s disease by erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus mycelia pilot double-blind placebo-controlled study[J].Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 2020, 12:155.
[49] ![]() -KOCIUBA I, TRZECIAK-RYCZEK A, KUPNICKA P, et al.Neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects of Hericium erinaceus[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(21):15960.
-KOCIUBA I, TRZECIAK-RYCZEK A, KUPNICKA P, et al.Neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects of Hericium erinaceus[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(21):15960.
[50] ZHANG C-C, CAO C-Y, KUBO M W, et al.Chemical constituents from Hericium erinaceus promote neuronal survival and potentiate neurite outgrowth via the TrkA/Erk1/2 pathway[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2017, 18(8):1659.
[51] LIN C-Y, CHEN Y-J, HSU C H, et al.Erinacine S from Hericium erinaceus Mycelium promotes neuronal regeneration by inducing neurosteroids accumulation[J].Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 2023, 31(1):32-54.
[52] LEE K F, HSIEH Y Y, TUNG S Y, et al.The cerebral protective effect of novel erinacines from Hericium erinaceus Mycelium on in vivo mild traumatic brain injury animal model and primary mixed glial cells via Nrf2-dependent pathways[J].Antioxidants, 2024, 13(3):371.
[53] MORI K, INATOMI S, OUCHI K Z, et al.Improving effects of the mushroom Yamabushitake (Hericium erinaceus) on mild cognitive impairment:A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial[J].Phytotherapy Research, 2009, 23(3):367-372.
[54] ![]() BIZJAK M, JENKO PRAŽNIKAR Z, KENIG S, et al.Effect of erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus supplementation on cognition:A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study[J].Journal of Functional Foods, 2024, 115:106120.
BIZJAK M, JENKO PRAŽNIKAR Z, KENIG S, et al.Effect of erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus supplementation on cognition:A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study[J].Journal of Functional Foods, 2024, 115:106120.
[55] CORDARO M, SALINARO A T, SIRACUSA R, et al.Key mechanisms and potential implications of Hericium erinaceus in NLRP3 inflammasome activation by reactive oxygen species during Alzheimer’s disease[J].Antioxidants, 2021, 10(11):1664.
[56] PRASHER P, SHARMA M, SHARMA A K, et al.Key oncologic pathways inhibited by Erinacine A:A perspective for its development as an anticancer molecule[J].Biomedicine &Pharmacotherapy, 2023, 160:114332.
[57] KUO H C, KUO Y R, LEE K F, et al.A comparative proteomic analysis of Erinacine A’s inhibition of gastric cancer cell viability and invasiveness[J].Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 2017, 43(1):195-208.