微生物污染是引起食物中毒和动植物病疫的主因之一,国家标准检测方法主要通过传统培养结合生理生化鉴定,其检测过程一般需要3~6 d,不但耗时耗力,且对技术条件要求较高,无法满足政府与企业倡导的快速简便需求,开发新型快速检测技术成为当务之急。快速检测技术相对传统培养法和依赖仪器检测而言,其最大特点是简便快速,不依赖精密仪器的辅助,检测时间短等。目前常用的快速检测方法有化学比色法、酶抑制技术、分子生物学检测技术与生物芯片技术等。其中,分子生物学检测技术以其灵敏度高、漏检率低、窗口期检测时间短等优点在常规快速检测技术中占明显优势,其主要通过“核酸提取-扩增-检测”三步操作对核酸分子的精确鉴定,从而提供各类风险源以及疫病检出的相关信息,为其预防、监控和治疗提供有效依据。聚合酶链式反应(polymerase chain reaction,PCR)自20世纪80年代引入以来,已作为分子生物学研究的重要手段,广泛应用于生命科学和环境科学等领域中[1-2]。然而,由于PCR技术及其衍生技术均存在对温控设备的依赖性高、热循环过程耗时与操作专业化等特点,其应用范围受限;而与之相比,重组酶等温扩增技术只需温度调控,无需特殊仪器辅助,易于实现扩增和现场检测。
重组酶等温扩增技术是一种新型的体外核酸等温扩增技术,其扩增原理是各种酶在腺嘌呤核苷三磷酸(adenosione triphosphate,ATP)作用下,重组酶蛋白与寡核苷酸引物结合形成重组丝复合物,单链DNA结合蛋白通过链置换方式,将模板DNA解链,自身与单链DNA模板结合,防止在形成新链DNA之前母链聚集配对;随后,重组丝复合物扫描模板DNA单链,当识别到与之引物相互配对的序列时,负责碱基配对的重组酶蛋白可通过与单链DNA结合蛋白结合,阻截细胞核内核酸酶降解单链DNA[3];最后,DNA聚合酶在引物的3′端添加碱基进行DNA复制延伸。重组酶等温扩增技术反应机制如图1所示。
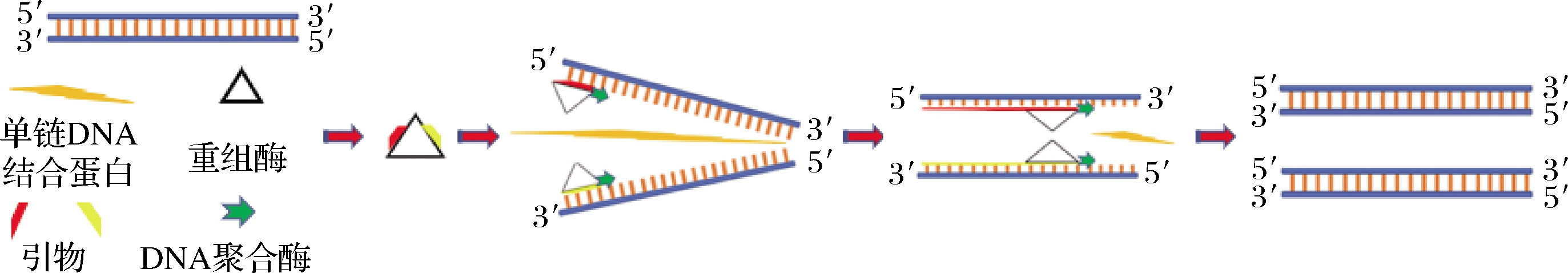
图1 重组酶等温扩增技术反应机制
Fig.1 Reaction mechanism of isothermal recombinase amplification
目前,重组酶等温扩增技术包括RPA(recombinase polymerase amplification)和RAA(recombinase aided amplification)2种技术[4-5],其不同之处在于RAA是细菌或真菌中获得的重组酶来替代RPA技术中较难获得的噬菌体重组酶,两者整个扩增过程一致,通过结合、链置换、延伸实现体外DNA扩增。现有研究表明,RPA与RAA技术能在恒定或较宽温度范围内,通过30 min左右自动循环的动态环境,可实现微量核酸在体外高效快速扩增,再由端点检测法对扩增产物进行检测,即可得到理想检测结果[6]。近年来,随着研究人员对分析检测效率与准确度要求的逐年提升,RPA与RAA技术在分析检测领域中得到较广泛的应用。本文在简述RPA与RAA技术扩增原理的基础上,重点阐述了重组酶等温扩增技术在病毒与细菌检测、动植物检验检疫、食品安全等方面的应用研究进展,提出存在问题与解决办法,展望了其未来发展前景,以期为后期RPA与RAA技术应用领域的拓展提供理论参考。
1 重组酶等温扩增技术在分析检测中的应用研究进展
RPA技术发展至今已有10余年,其应用领域比RAA技术广泛,尤其在现场检测方面中发挥着重要的作用。RAA作为一种新型的具有我国自主知识产权的等温核酸扩增技术,其重组酶来源广泛,使等温扩增技术得以丰富,更充实了体外核酸扩增技术的发展。2项技术在病毒与细菌检测、动物检验检疫与食品安全等领域中得到广泛应用。
1.1 病毒检测
手足口病是严重公共卫生问题引起的主要传染病,主要特征表现为口腔黏膜疱疹或溃疡和手、足部出疹等,其主要由20多种肠道病毒引起,以柯萨奇病毒CA16型和肠道病毒EV71型最常见,也有柯萨奇病毒CA6型和CA10型引起的症状[7]。采用RPA与RAA技术可实现该病毒的快速准确检测。其中,YIN等[8]使用实时Real-time-RPA(RT-RPA)技术检测EV71,在临床样品评估中得出该检测技术与RT-qPCR差异不大,但检测精度明显提高,且时间短;LI等[9]通过RT-RAA技术可在42 ℃条件下,30 min高灵敏检测到EV71与CA16,临床诊断特异性高;WANG等[10]建立了RT-RPA技术快速检测柯萨奇病毒CA-A6的方法;YAN等[11]建立RT-RAA技术检测柯萨奇病毒CA-A6和CA-A10,检测结果与RT-qPCR一致,特异性高达100%,在监测感染与疫情控制中均具潜在价值。在其他病毒检测方面,SHEN等[12]通过热处理粗提基因组DNA,用RT-RAA法30 min内可检测到乙型肝炎病毒,该病毒与人类免疫缺陷病毒和丙型肝炎病毒无交叉反应;BAI等[13]通过热处理粗提基因组DNA,建立了RT-RAA法结合内部控制对照及RAA技术与侧流层析试纸条(lateral-flow dipstick, LFD)双重检测,能有效消除假阳性结果;此外,呼吸道合胞病毒是一种能在全球范围内引起婴幼儿下呼吸道感染的病原体,有学者通过RT-RAA技术[14]和RT-RPA技术[15]提高灵敏度快速检测到呼吸道合胞病毒,表现出很大的检测应用潜力。
1.2 细菌检测
由于传统检测方法存在费时、检测精度不高等缺点,对细菌污染引起的伤口感染、食物污染、因动物携带造成的交叉感染等得不到及时控制,检测部门对快速检测技术的需求日益增多。RPA技术起初由PIEPENBURG等[3]提出,将其用于检测耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌的特异基因,可检测到低至10个拷贝模板;目前,RPA与RAA技术已广泛应用于副溶血性弧菌、大肠杆菌与金黄色葡萄球菌等检测中。其中,孙晓红等[16]建立了RAA-LFD技术检测副溶血性弧菌的方法,并对检测条件进行了优化,获得反应温度为37 ℃,扩增时间为20 min的最佳反应条件。该方法检测灵敏度比常规PCR高10倍数量级,为现场或低资源环境中检测副溶血性弧菌提供了一种简便、快速、特异灵敏的方法;魏莹等[17]对易引起人和动物感染性疾病的病原体A族乙型溶血性链球菌通过RAA技术在恒定温度下,20 min内实现快速检测;DU等[18]将RPA技术在37~42 ℃扩增单核细胞增生李斯特菌目的基因,扩增产物可直接用LFD肉眼观察;周广彪等[19]建立基于RPA的检测方法特异性好,不需要任何仪器辅助,只在人体温度的条件下特异性扩增就可得到拟态弧菌的特异性目的条带,其灵敏度与常规PCR法一致。
1.3 动物检验检疫
血吸虫病是一种能引起人和动物共感染的寄生虫病,卫生部报告显示,近年来国家在控制血吸虫病方面进展缓慢[20],原因在于缺乏有效的诊断方法来监测低强度感染与评估干预效果。因此,开发有效的快速检测手段势在必行[21-22]。SONG等[23]建立了RAA检测日本血吸虫特异性基因片段的新方法,可在30 min内简便快速检测到最低检测模板为20拷贝或0.5 ng基因组DNA;SUN等[24]通过RPA-LFD技术快速直观检测到日本血吸虫,为评价其有效性,与酶联免疫吸附试验和间接血凝试验进行比较,发现RPA-LFD技术的灵敏性和特异性均高于另外2种,在现场应用中潜力良好;唐慧骥等[25]通过建立的RAA方法检测发现新菠萝灰粉蚧带来的危害,具有耗时短,特异性区分效果好,适于检验人员快速检测筛查;周鸿让等[26-27]根据多房棘球绦虫线粒体基因序列设计特异性引物进行RAA扩增后,通过琼脂糖凝胶电泳(agarose gel electrophoresis,AGE)检测,能快速高效区分多房棘球绦虫与其他寄生虫,并通过建立双重RAA方法成功检测多房棘球绦虫的2种类型,为多房棘球绦虫虫种鉴定与棘球蚴病基因诊断提供有效的技术支撑。
1.4 食品安全
食品安全一直是消费者关注的焦点。2013年欧洲爆发的“马肉风波”[28],用猪肉制作假牛肉干和牛肉丸子[29]行为欺骗消费者,扰乱市场。早期有基于环介导等温扩增(loop-mediated isothermal amplification, LAMP)和等温扩增荧光(isothermal amplification fluorescent technology, IAFT)技术应用到动物源性掺假检测中,但其所需引物复杂、操作繁琐[30-32]。部分研究者将RPA技术应用于肉类和转基因等方面检测,在实际检测中获得了良好的效果。如郭燕华等[33]以牛源性线粒体细胞色素b基因建立了特异性RPA检测方法,其灵敏度可达0.1 ng/μL,可用于市售生鲜肉制品及加工肉制品中牛源性成分鉴定;林霖等[34]基于细胞色素C氧化酶亚型I中的猪特异性DNA序列结合核酸快速提取方法,建立RT-RPA快速检测法,可检出低至1%(质量分数)的猪肉含量,对牛肉中是否掺有猪肉成分达到较好的区分。
商业化种植转基因作物会让一些利益分子乘虚而入,将用作饲料和其他用途的转基因作物掺入到消费者的食品中。因此,有必要在转基因农作物检测领域开发快速高效、易于携带的检测装备。其中,刘静等[35]根据外源基因草丁膦乙酰转移酶基因与载体骨架连接区序列设计引物建立RPA检测转基因玉米Bt11的方法,检测限远低于欧盟国家设定的转基因最低限量0.9%,灵敏度高,可满足相关行业的日常检测需求;谢实龙[36]建立RT-RPA快速筛查体系,能高灵敏度地检出最低48拷贝数的模板。该技术在实际样品筛查中,能提供稳定可靠结果,在转基因成分检测中具有广泛的应用价值。
2 存在问题与解决办法
重组酶等温扩增技术具有不受场地限制与检测时间短等优点,是一种理想可推广的快速检测方法。RPA与RAA技术作为新型重组酶等温扩增技术,仍存在部分缺点。如重组酶等温扩增技术分析易受多种因素影响。内因主要包括酶活性、引物探针设计等,外因主要包括产物检测前处理、反应温度和假阴性问题等。此外,固定反应体系和较高试剂成本也影响其普适性。
2.1 酶促反应
重组酶等温扩增技术主要借助重组酶、单链DNA结合蛋白与DNA聚合酶等3种核心酶的协同作用完成扩增反应,其对蛋白酶活性要求较高,一方面需要保证反应体系中酶活性,任何一种酶失活都会导致扩增失败;另一方面需要保证反应体系中各种酶接触充分,有效反应才能促进产物形成,提高反应效率。反应后的产物检测方法多样,主要有AGE[29,37]、RT-RAA和RT-RPA[38-39]、LFD[40]与联动CRISPR/Cas系统[41]等。但反应结束后的体系中存在大量蛋白酶,若在进行AGE前不做处理,电泳结束后成像观察有抹带现象,影响目的条带观察。因此,重组酶等温扩增产物在进行AGE前需要通过高温使蛋白变性失活,离心取上清液进行检测[42];同时,通过加入酚-氯仿-异戊醇进行纯化处理,检测其上清液[43]。
2.2 引物探针设计
一个良好的核酸扩增关键在于引物与探针设计,根据引物设计原则,设计引物长度应在30 bp左右,过长或过短均会影响扩增速度和检测灵敏度;扩增片段应在80~500 bp,以保证扩增反应的快速灵敏且有效。若样品需要定时定量,可在该反应体系中添加探针,探针位置应位于上下游引物中间,设计时尽量避免下游引物和探针的重叠,减少影响扩增效率与产生非特异性信号的二聚体形成。最新开发的一款基于Python的软件包[44]能自动创建和过滤RPA引物和探针对,其对比几个序列识别保守目标,并过滤与可能背景生物交叉反应区域。但其使用需要一定的程序编辑基础,这无疑给工作人员在筛选优化引物序列时增加技术难度,降低效率。因此,特异性引物设计需自行摸索,筛选合适引物对进行扩增。其中,MOHAMMAD等[45]针对园艺作物设计了18对长度为18~28 bp的引物,发现有4对引物能成功扩增7种园艺作物的DNA。因此,有必要加强引物选择,开发能替代手动设计的软件来筛选最佳核苷酸引物对与探针。
2.3 反应温度
重组酶等温扩增反应可在较宽的温度范围内高效完成(<40 min)。RAA与RPA技术主要借助酶的活性来完成扩增,选择最佳温度是快速得到扩增产物的前提。相关研究显示[8,19,46],RPA与RAA技术反应温度接近人体温度,不依赖温控设备,其在未来将会成为一种行之有效的自测手段,快速检测人体自身的一些样本。
2.4 假阴性问题
核酸材料被污染是影响分析结果准确性的关键,采取有效措施加以预防、避免至关重要。因此,扩增前后的区域应分开、使用带滤芯的枪头、使用完的材料应收集到密闭容器与在通风橱进行操作均能提高检测准确度。扩增得到的产物若要进行AGE或LFD等的开盖检测,势必会引起气溶胶污染,影响检测结果,给实验带来一定误差。在实验过程中进行高温或酚/氯仿纯化处理,仍会带来一定影响。对此可将核酸扩增试剂管与检测试剂管组装,在一个密封的环境中完成检测,避免了开盖操作引起的气溶胶污染问题,能提高现场即时检测的准确性[47]。
抑制剂或食品基质的影响会使检测结果出现假阴性,影响结果判断,从而进一步限制该技术在现场中的应用。根据检测对象添加一段看家基因序列作为扩增内标(internal amplification control,IAC),与目标基因同步扩增。若检测结果只有IAC条带没有目标基因条带,可判定为阴性,若检测结果都没有IAC条带和目标基因条带,可判定反应受到干扰或污染,出现假阴性,需重新进行检测,从而降低假阴性风险,提高检测准确度[48-49]。
2.5 使用成本
目前,市售的RAA和RPA技术都使用试剂盒,其反应体系已固定,会使用户使用灵活性明显降低,体系更改必然会引起污染问题,影响其普适性;作为具有自主知识产权保护的技术,成本相对较高等问题需要进一步完善,通过研发出低廉、高效的酶制剂降低成本是行之有效的手段。
3 前景与展望
重组酶等温扩增技术作为在恒定温度条件下反应的新型核酸体外扩增技术,其具有冻干粉形式易于运输、灵敏度高、特异性强、反应时间快、操作简单等优点,逐渐被人们认可为一种“可替代PCR的技术”。虽然RAA与RPA技术还存在一定局限性,但这种重组酶等温扩增技术填补了传统培养和依赖温变设备技术外的空缺,这种新技术能在现场和非实验室环境实现即时检测,具有潜在优势。相比较RPA来说,RAA重组酶来源相对广泛,且是我国自主研发的新型等温核酸扩增技术,符合我国快速检测的需求。相信在不久的将来,研究人员将能在了解和完善反应机制的同时,使RAA与RPA扩增技术在研究和现场检测中发挥更大价值,实现“核酸提取-扩增-检测”三步一体化的操作。未来重组酶等温扩增技术的发展方向和研究热点将在小型化、便携式仪器的基础上,会在数字RPA、数字RAA和多通道检测方面实现新的突破,将在低资源环境、部分医疗点和需求点等疾病突发地得到广泛的推广应用。
[1] 李聪,刘健慧,李志辉, 等.4种食源性致病菌的多重PCR快速检测方法研究[J].食品研究与开发, 2019, 40(21):164-169.
LI C, LIU J H, LI Z H, et al.Study on multiplex PCR of rapid detection method for four foodborne pathogens[J].Food Research and Development, 2019, 40(21):164-169.
[2] 崔丙健,高峰,胡超, 等.不同再生水灌溉方式对土壤-辣椒系统中细菌群落多样性及病原菌丰度的影响[J].环境科学, 2019, 40(11):5 151-5 163.
CUI B J, GAO F, HU C, et al.Effect of different reclaimed water irrigation methods on bacterial community diversity and pathogen abundance in the soil-pepper ecosystem[J].Environmental Science, 2019, 40(11):5 151-5 163.
[3] PIEPENBURG O, WILLIAMS C H, STEMPLE D L, et al.DNA detection using recombination proteins[J].Plos Biology, 2006, 4(7):e204.
[4] LÜ B, CHENG H R, YAN Q F, et al.Recombinase-aid amplification: A novel technology of in vitro rapid nucleic acid amplification[J].Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2010, 40:983-988.
[5] KUZMINOV A.DNA replication meets genetic exchange:Chromosomal damage and its repair by homologous recombination[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2001, 98(15):8 461-8 468.
[6] WANG Z, YANG P P, ZHANG Y H, et al.Development of a reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral-flow dipstick assay for avian influenza H9N2 HA gene detection[J].Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 2018, 66(1):546-551.
[7] 鲍金圭,李崇建,江慧,等.2016-2018年钦州市手足口病住院患儿病原学检测结果分析[J].检验医学与临床, 2019, 16(24):3 592-3 595.
BAO J G, LI C J, JIANG H, et al.The pathogenic composition of hospitalized children with hand, foot and mouth disease in Qinzhou during 2016-2018[J].Laboratory Medicine and Clinic, 2019, 16(24):3 592-3 595.
[8] YIN D, ZHU Y N, WANG K F, et al.Development and evaluation of a rapid recombinase polymerase amplification assay for the detection of human enterovirus 71[J].Archives of Virology, 2018, 163(9):2 459-2 463.
[9] LI X N, SHEN X X, LI M H, et al.Applicability of duplex real time and lateral flow strip reverse-transcription recombinase aided amplification assays for the detection of Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus A16[J]. Virology Journal, 2019, 16(1):166.
[10] WANG K F, WU Y, YIN D, et al.Development and evaluation of a rapid recombinase polymerase amplification assay for detection of coxsackievirus A6[J]. Archives of Virology, 2017, 162(1):287-290.
[11] YAN T F, LI X N, WANG L, et al.Development of a reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for the detection of coxsackievirus A10 and coxsackievirus A6 RNA[J].Archives of Virology, 2018, 163(6):1 455-1 461.
[12] SHEN X X, QIU F Z, SHEN L P, et al.A rapid and sensitive recombinase aided amplification assay to detect hepatitis B virus without DNA extraction[J].BMC Infectious Diseases, 2019, 19(1):229.
[13] BAI X D, MA X J, LI M H, et al.Field applicable detection of hepatitis B virus using internal controlled duplex recombinase-aided amplification assay and lateral flow dipstick assay[J].Journal of Medical Virology, 2020,92(12);3 344-3 353.
[14] QI J J, LI X N, ZHANG Y, et al.Development of a duplex reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for respiratory syncytial virus incorporating an internal control[J].Archives of Virology, 2019, 164(7):1 843-1 850.
[15] XI Y, XU C Z, XIE Z Z, et al.Development of a reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of human respiratory syncytial virus[J].Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2019, 45:8-13.
[16] 孙晓红,后来旺,郜蓉.一种重组酶等温扩增技术检测副溶血性弧菌的方法:中国, CN 110564881A [P].2019-10-21.
SUN X H, HOU L W, GAO R.Method for detecting Vibrio parahaemolyticus by isothermal recombinase aided amplification:China, CN 110564881A [P].2 019-10-21.
[17] 魏莹,郭利川,张小平,等.重组酶介导扩增方法快速检测A族乙型溶血性链球菌[J].中国国境卫生检疫杂志, 2018, 41(5):314-316;323.
WEI Y, GUO L C, ZHANG X P, et al.Establishment of recombinase aided amplification assay for group A streptococcus pyogens detection[J].Chinese Journal of Frontier Health and Quarantine, 2018, 41(5):314-316;323.
[18] DU X J, ZANG Y X, LIU H B, et al.Recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow strip for Listeria monocytogenes detection in food[J].Journal of Food Science, 2018, 83(4):1 041-1 047.
[19] 周广彪,段建发,胡晓珊, 等.重组酶聚合酶扩增技术(RPA)检测拟态弧菌[J].检验检疫学刊, 2018, 28(5):1-4;16.
ZHOU G B, DUAN J F, HU X S, et al.Detection of Vibrio Mimicus heat-labile hemolysin by recombinase polymerase amplification[J].Journal of Inspection and Quarantine, 2018, 28(5):1-4;16.
[20] LI S Z, ZHENG H, GAO J, et al.Endemic status of schistosomiasis in the People’s Republic of China in 2012[J].Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control, 2013, 25(6):557-563.
[21] BERGQUIST R, JOHANSEN M V, UTZINGER J.Diagnostic dilemmas in helminthology:What tools to use and when? [J].Trends in Parasitology, 2009, 25(4):151-156.
[22] 银娜,梁俊,高志贤.银纳米簇用于食品包装污染物的检测及其抗菌性能的应用[J].包装工程, 2019, 40(21):44-50.
YIN N, LIANG J, GAO Z X.Silver nanoclusters for the detection of food packaging contaminants and their application in antibacterial properties[J].Packaging Engineering, 2019, 40(21):44-50.
[23] SONG Z, TING L, KUN Y, et al.Establishment of a recombinase-aided isothermal amplification technique to detect Schistosoma japonicum specific gene fragments[J].Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control, 2018, 30(3):273-277.
[24] SUN K, XING W, YU X, et al.Recombinase polymerase amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick for rapid and visual detection of Schistosoma japonicum[J].Parasite Vectors, 2016, 9(1):476.
[25] 唐慧骥,党志浩,郭长宁,等.应用重组酶介导核酸扩增技术快速鉴定新菠萝灰粉蚧[J].植物检疫, 2019, 33(2):37-42.
TANG H J, DANG Z H, GUO C N, et al.Rapid detection for Dysmicoccus neobrevipes by recombinase-aid amplification[J].Plant Quarantine, 2016, 9(1):476.
[26] 周鸿让, 陈木新, 余晴, 等.重组酶介导的等温核酸扩增技术检测多房棘球绦虫方法的建立及初步应用[J].中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2020, 32(2):168-173;180.
ZHOU H R, CHEN M X, YU Q, et al.Establishment of a recombinase-aided isothermal amplification assay for nucleic acid detection of Echinococcus multilocularis and its preliminary application[J].Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control, 2020, 32(2):168-173;180.
[27] 周鸿让,茅光耀,王晓玲,等.重组酶介导的多重核酸等温扩增法鉴别细粒棘球绦虫G1和多房棘球绦虫技术的建立与应用[J].中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2020,38(3):310-316.
ZHOU H R, MAO G Y, WANG X L, et al.Establishment and application of a multiplex recombinase-aided isothermal amplification technique for identifying Echinococcus granulosus G1 and Echinococcus multilocularis[J].Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases, 2020,38(3):310-316.
[28] 佚名. 温州警方查获制售假牛肉干案一年销售达百万元[J].中国防伪报道, 2017(5):85-86.
YI M.Police in Wenzhou have uncovered a case in which fake beef jerky was sold for up to one million yuan a year[J].China Anti-Counterfeiting Report, 2017(5):85-86.
[29] 韩利. 牛丸无牛肉虾丸中掺鸭 成都一公司掺假掺杂被罚40万[J].广西质量监督导报, 2016(12):35-36.
HAN L.A company in Chengdu was fined 400,000 yuan for adulterating beef and shrimp balls[J].Guangxi Quality Supervision Guide Periodical, 2016(12):35-36.
[30] 王耕,张薇,陈安东,等.肉类食品的动物物种基因鉴别及等温扩增荧光(IAFT)快速检测技术的建立[J].生物化工, 2016, 5(2):21-25.
WANG G, ZHANG W, CHEN A D, et al.Identification of animal species in meat food and establishment of rapid detection technology for isothermal amplification of fluorescence (IAFT) [J].Biological Chemical Engineering, 2016, 5(2):21-25.
[31] 肖蕾,蓝蔚青,孙晓红,等.金枪鱼常用保鲜方式及品质检测技术研究进展[J].包装工程, 2017, 38(5):115-120.
XIAO L, LAN W Q, SUN X H, et al.Research progress in commonly used preservation methods and quality detection techniques of Tuna[J].Packaging Engineering, 2017, 38(5):115-120.
[32] SUN X H, XU Q, PAN Y J, et al.A loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood[J].Annals of Microbiology, 2012, 62(1):263-271.
[33] 郭燕华,王德莲,王强,等.重组酶介导等温扩增技术快速检测牛肉及牛肉制品中的牛源性成分[J].食品安全质量检测学报, 2017, 8(5):1 745-1 749.
GUO Y H, WANG D L, WANG Q, et al.Determination of bovine ingredient in beef and its derivates with recombinase polymerase mediated isothermal amplification[J].Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2017, 8(5):1 745-1 749.
[34] 林霖,冯荣虎,王坤,等.牛肉真伪鉴别荧光RPA现场快检方法建立[J].食品科技, 2018, 43(6):322-326.
LIN L, FENG R H, WANG K, et al.Construct beef authentication on-site rapid detection method based on fluorescent RPA technology[J].Food Science and Technology, 2018, 43(6):322-326.
[35] 刘静,武国干,吴潇,等.重组酶聚合酶扩增技术快速检测转基因玉米Bt11[J].上海农业学报, 2018, 34(1):20-24.
LIU J, WU G G, WU X, et al.Rapid detection of genetically modified maize Bt11 by recombinase polymerase amplification assay[J].Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 2018, 34(1):20-24.
[36] 谢实龙. 转基因成分重组酶聚合酶扩增(RPA)快速检测方法的建立[D].阜阳:阜阳师范学院, 2019.
XIE S L.The application of recombinase polymerase amplification technology in transgenic detection [D].Fuyang:Fuyang Normal University, 2019.
[37] 廖新辉,易浔飞,崔智慧,等.用重组酶介导等温核酸扩增技术检测烟曲霉[J].临床检验杂志, 2015, 33(3):214-218.
LIAO X H, YI X F, CUI Z H, et al.Detection for Aspergillus fumigatus by recombinase polymerase amplification assay[J].Chinese Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science, 2015, 33(3):214-218.
[38] 刘爽,黄广涛,龚雅利, 等.基于重组酶聚合酶扩增技术建立实时荧光法快速检测鲍曼不动杆菌的研究[J].中国病原生物学杂志, 2019, 14(3):311-314.
LIU S, HUANG G T, GONG Y L, et al.Rapid detection of Acinetobacter baumannii by real-time fluorescence method based on recombinase polymerase amplification[J].Journal of Pathogen Biology, 2019, 14(3):311-314.
[39] 黄纪徽,吴山楠,王丹云, 等.虾肝肠胞虫实时荧光RAA快速检测方法的建立[J].养殖与饲料, 2018(11):13-16.
HUANG J H, WU S N, WANG D Y, et al.Establishment of a fast real-time recombinase aided amplification detection method for shrimp Hepatocellular cytospora[J].Animals Breeding and Feed, 2018(11):13-16.
[40] MA B, FANG J, LIU W, et al.A simple and efficient method for potential point-of-care diagnosis of human papillomavirus genotypes:Combination of isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification with lateral flow dipstick and reverse dot blot[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2019, 411(28):7 451-7 460.
[41] CHEN J S, MA E, HARRINGTON L B, et al.CRISPR-Cas12a target binding unleashes indiscriminate single-stranded DNase activity[J].Science, 2018, 360(6 387):436-439.
[42] LIU H B, ZANG Y X, DU X J, et al.Development of an isothermal amplification-based assay for the rapid visual detection of Salmonella bacteria[J].Journal of Dairy Science, 2017, 100(9):7 016-7 025.
[43] 王亚磊,张海洋,王权,等.产单核细胞李氏杆菌RPA-LF快速检测方法的建立[J].中国兽医科学, 2020, 50(1):1-9.
WANG Y L, ZHANG H Y, WANG Q, et al.Rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes with isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow analysis[J].Chinese Veterinary Science, 2020, 50(1):1-9.
[44] HIGGINS M, RAVENHALL M, WARD D, et al.PrimedRPA:Primer design for recombinase polymerase amplification assays[J].Bioinformatics, 2019, 35(4):682-684.
[45] MOHAMMAD U, TEIXEIRA DA SILVA J, Zou Y Y, et al.Successful amplification of DNA using recombinase-aided amplification (RAA) and its application to seven horticultural crops[J].Biotechnology, 2016, 2(12):7.
[46] ZACHARY A C, BRITTANY R, REBECCA R K.Equipment-free incubation of recombinase polymerase amplification reactions using body heat[J].PloS One, 2014, 9(11):e112 146.
[47] 杭州优思达生物技术有限公司. 一种核酸一体化检测方法及检测试剂管:中国, CN 108796038A [P].2018-06-26.
Hangzhou Ustar Biotechnologies .The invention relates to a nucleic acid integration detection method and a detection reagent tube:China, CN 108796038A [P].2018-06-26.
[48] 李伟,庄濠宇,温尔英,等.添加扩增内标的重组酶聚合酶扩增技术(RPA-IAC)检测创伤弧菌[J].检验检疫学刊, 2019, 29(3):5-8.
LI W, ZHUANG H Y, WEN E Y, et al.Recombinant enzyme polymerase amplification (RPA-IAC) with amplified internal standard for detection of Vibrio vulnificus[J].Journal of Inspection and Quarantine, 2019, 29(3):5-8.
[49] YANG H L, WEI S, GOONERATNE R, et al.Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification assay for Vibrio parahaemolyticus detection with an internal amplification control[J].Canadian Journal of Microbiology,2018, 64(4):223-230.