样品前处理是检测分析技术的重要环节,快速简单、环保、微型化是方向发展。分散液液微萃取技术(dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction,DLLME)集采样、萃取和浓缩于一体,具有简单、廉价、快速、富集倍数高、有机溶剂或离子液体(ionic liquid,IL)用量少等特点[1]。但是传统的DLLME需要使用三氯甲烷、四氯乙烷、芳香烃类IL等毒性大和环境不友好的液体作为提取溶剂。
深共晶溶剂(deep eutectic solvents,DESs),包括天然深共晶溶剂(natural deep eutectic solvents,NaDESs),当构成DESs的化合物是初级代谢物(有机酸、糖、氨基酸或胆碱衍生物)时,DESs就被称为NaDESs,在室温下呈液态,由氢键供体(hydrogen bond donor,HBD)和氢键受体(hydrogen bond acceptor,HBA)合成,具有毒性低、性质可调、可回收和对环境友好等优点[2]。DESs代替传统的有机溶剂和IL,可以避免毒性大和环境污染的问题,制备来源广泛且廉价,因此被称为“21世纪的新型绿色溶剂”[2]。
DESs与DLLME相结合,可以充分发挥两者的优势,形成萃取和浓缩一体化的绿色环保新技术,具有操作简单、回收率高、富集倍数高、预处理微型化等特点。2015年,KHEZELI等[3]和KARIMI等[4]最早将DESs与DLLME相结合,建立了深共晶溶剂-分散液液微萃取技术(deep eutectic solvents-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction,DESs-DLLME),并分别应用于水样中多环芳香烃和食用油中Pb、Cd元素的分析检测。此后,关于DESs-DLLME技术在检测污染物方面的研究相继出现,如图1所示。本文简要介绍DESs的性质,重点对 DESs-DLLME不同模式间的优劣进行分析比较和综述其在食品及环境污染物检测中的应用,以期为DESs-DLLME的发展和应用提供参考。
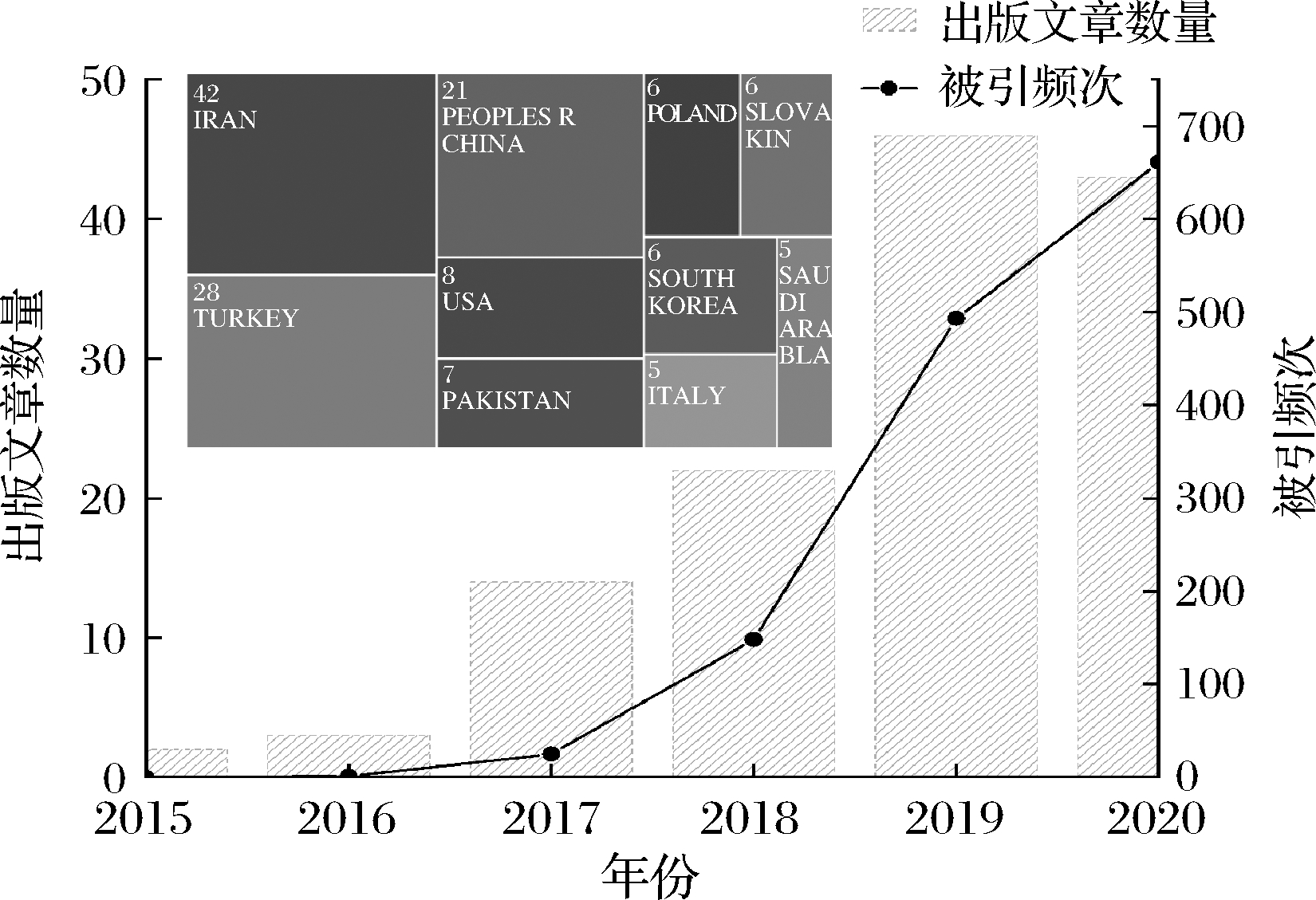
图1 DESs-DLLME技术近6年来出版文章数量趋势、
被引频次趋势和各国出版文章数量分布
Fig.1 The trend of the number of published articles, citation frequency and the distribution of the number of published articles in various countries regarding DESs-DLLME in the past six years
注:图中数据来源于Web of Science
1 深共晶溶剂与分散液液微萃取联用技术概述
1.1 DESs-DLLME的原理
DESs-DLLME的原理是DESs在分散剂(或借助外部条件达到分散的目的)的作用下形成细小的液滴,均匀分散在含有目标物的样品溶液中,形成样品溶液-分散剂-DESs乳浊液体系,目标物不断地被萃取到DESs相中并快速达到平衡。经离心、冷却或凝固后,目标物被富集在离心管顶部或底部DESs相中,利用注射器取出含目标物的DESs相并进行仪器分析。图2阐述了DESs-DLLME的操作步骤。
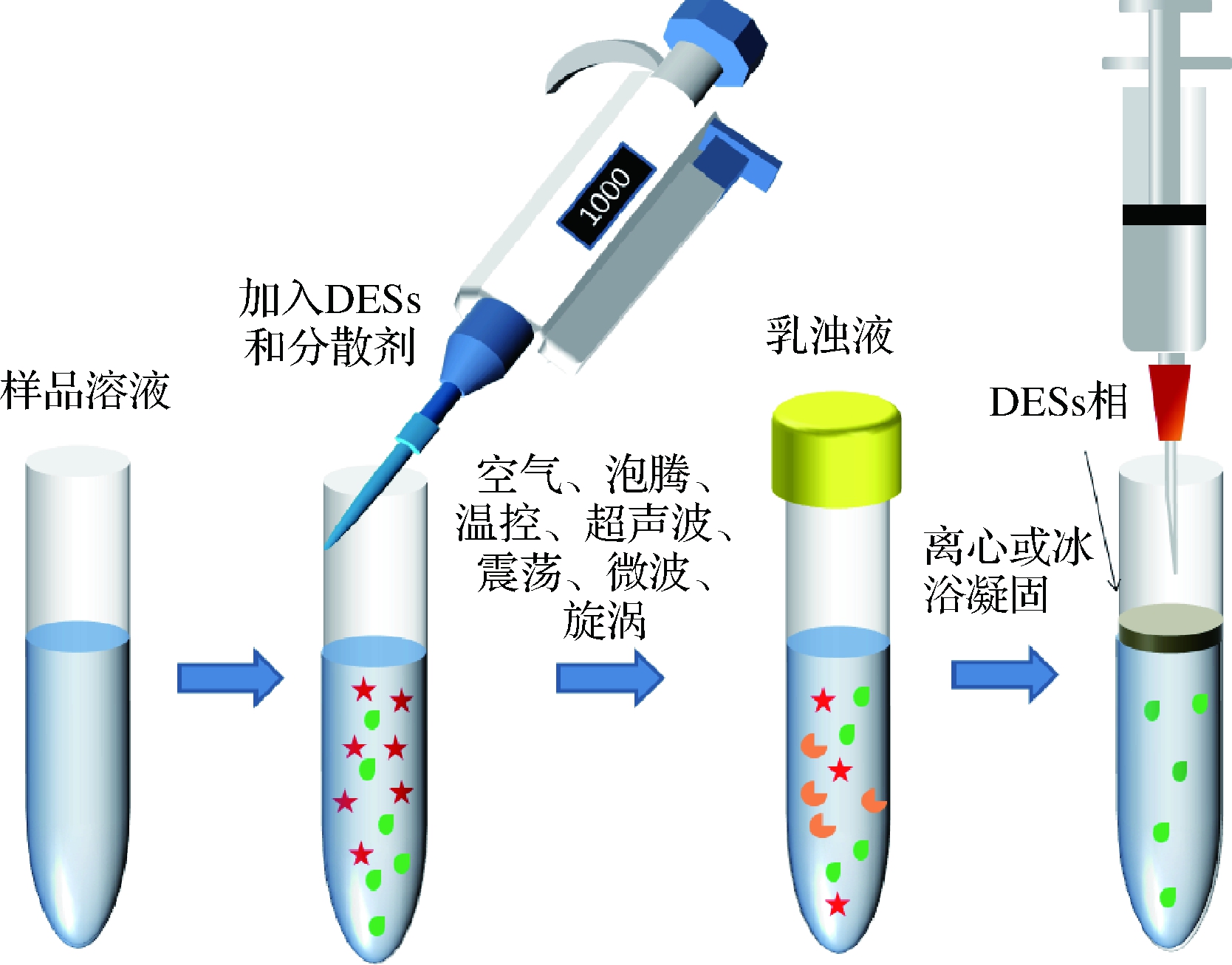
图2 DESs-DLLME的操作过程
Fig.2 Flow chart of DESs-DLLME
对DESs-DLLME而言,科学选择萃取剂和分散剂可以提高提取效率。萃取剂的选择应满足与水相比,密度有差异、对目标物亲和性高和有优良的色谱行为。常用的萃取剂主要有以氯化胆碱(choline chloride,ChCl)等季铵盐为HBA合成的亲水性DESs和以薄荷醇或百里香酚为HBA合成的疏水性DESs。而分散剂的选择要同时满足溶于DESs和样品溶液,才能保证可在样品溶液中分离DESs液滴,常用的分散剂主要有乙腈、表面活性剂、甲醇、丙酮、四氢呋喃(tetrahydrofuran,THF)、IL、DESs。
1.2 DESs的性质
DESs最突出的性质是饱和蒸汽压低、极性范围广、性质可调等。(1)熔点由分子结构对称性、氢键和范德华力决定,DESs中阳离子和阴离子之间微弱的晶体格能导致熔点降低,HBD的比率决定DESs的熔点。(2)密度是DESs的一个非常重要物理参数,决定其在萃取目标物基质中的扩散性和溶解度。大部分DESs的密度比水的密度大,而HBD的结构对密度有显著影响,一般情况下,相同组分HBA/HBD的比值越大,密度越小。(3)DESs的高黏度归因于组分分子间强大的氢键网络,受HBD类型、盐类型以及它们的摩尔比影响,可通过加水和升高温度降低DESs黏度(η),且ηDESs >ηIL>η有机溶剂。(4)DESs的电导率与分子流动性呈线性关系,随温度升高而升高。DESs电导率低(室温下<2 mS/cm),组分的摩尔比对DESs的电导率影响较大。(5)表面张力与黏度相似,受DESs组分分子间相互作用的影响,和温度呈线性关系,随HBA浓度增大而减小。(6)DESs的极性范围广,取决于其组成及HBD的分子结构,随温度升高而减小和通过加水增加极性。(7)与有机溶剂和IL相比,合成DESs的各组分毒理特性较低,甚至无毒,且可生物降解,但DESs的毒性缺乏系统试验支撑[5-6],需要深入调查研究。
目前主要研究的DESs可分为3大类:亲水性DESs、准疏水性DESs和疏水性DESs,按HBD和HBA的构成不同可分为4种类型,即金属+有机盐、金属盐水合物+有机盐、HBD+有机盐和锌/AlCl3+HBD,其中由HBD+有机盐组成的DESs作为提取溶剂应用较多[7-9],多用于污染物分析检测。因此,可以通过改变DESs的性质来满足不同检测需要,扩大应用范围。
1.3 DESs-DLLME的模式
传统DESs-DLLME技术以DESs作为萃取剂,在分散剂的作用下进行扩散和有序排列,形成DESs/样品溶液/分散剂的萃取体系。以ChCl为HBA的DESs为例:Cl-形成的氢键指向外部亲水体系,其他疏水性基团互相作用构成疏水性内核,样品溶液中不同极性的成分吸附于DESs的不同部位或进入疏水性内核被DESs萃取。目前,研究人员对传统DESs-DLLME技术进行了改进,例如当DESs密度小于水时,借助空气或超声波辅助提高萃取效率[10-11],与目标物衍生法相结合[12-13]和借助外部条件(温控、沸腾等)而达到不需要使用分散剂[14-15]。LI等[5]总结了近年来DESs-DLLME的应用。本文将DESs-DLLME分为3种模式:传统DESs-DLLME,温控、超声波、振荡、微波、涡旋、空气、泡腾辅助DESs-DLLME和原位DESs-DLLME(in situ-DESs-DLLME)。
在3种模式中,传统DESs-DLLME是最简单的模式。在三元溶剂萃取体系(DESs-样品溶液-分散剂)中,不需要外界能量加速萃取,通过人工震荡或搅拌,离心后将含有目标物的DESs相从样品溶液中分离。但传统DESs-DLLME存在萃取目标物单一、提取效率低等问题,因此研究人员相继开发了空气辅助(air-assisted,AA)[16-17]、泡腾辅助(effervescence-assisted,EA)[18]、温控辅助(temperature-controlled-assisted,TCA)[19]、振荡辅助(shaker-assisted,SA)[20-21]、微波辅助(microwave-assisted,MA)[22]、涡旋辅助(vortex-assisted,VA)[23-24]、超声波辅助(ultrasound-assisted,UA)[25-26]DESs-DLLME模式。这些模式通过借助外界能量提高DESs在样品溶液中的溶解度,增大DESs液滴与目标物的接触面积,从而达到提高提取效率的效果。in situ-DESs-DLLME包含3种模型:(1)基于DESs的原位溶剂形成微萃取(deep eutectic solvents-in situ solvent formation microextraction,DESs-ISFME),该模式不需要预先合成DESs,在样品溶液中同时加入HBA和HBD,在外界能量条件下形成DESs,集DESs合成、萃取、含靶物的DESs相于一体,极大地缩短了萃取时间;(2)基于HBA或HBD与目标物形成DESs的原位溶剂微萃取(HBA or HBD-target-in situ solvent formation microextraction,HT-ISFME),该模式对于目标物具有非常高的选择性,尤其适用于复杂基质中目标物的提取;(3)基于DESs的原位分解萃取(deep eutectic solvents-in situ solvent decomposition microextraction,DESs-ISDME),该模式利用分解的不同组分分别充作萃取剂和分散剂的作用而达到微萃取平衡。目前,采用in situ-DESs-DLLME模式的研究中均不需要分散剂,3种DESs-DLLME模式的对比如表1所示。
表1 DESs-DLLME的3种模式
Table 1 Modes of DESs-DLLME
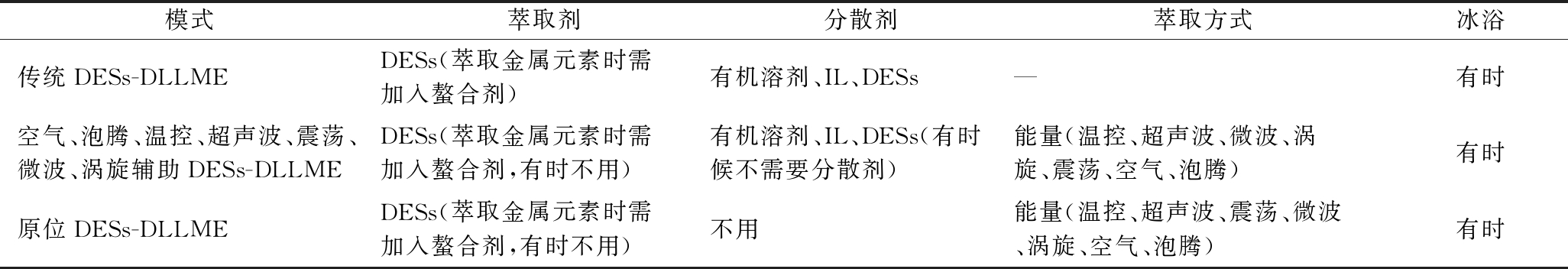
模式萃取剂分散剂萃取方式冰浴传统DESs-DLLMEDESs(萃取金属元素时需加入螯合剂)有机溶剂、IL、DESs—有时空气、泡腾、温控、超声波、震荡、微波、涡旋辅助DESs-DLLMEDESs(萃取金属元素时需加入螯合剂,有时不用)有机溶剂、IL、DESs(有时候不需要分散剂)能量(温控、超声波、微波、涡旋、震荡、空气、泡腾)有时原位DESs-DLLMEDESs(萃取金属元素时需加入螯合剂,有时不用)不用能量(温控、超声波、震荡、微波、涡旋、空气、泡腾)有时
注:—代表文中未提及(下同)
2 深共晶溶剂-分散液液微萃取在污染物检测中的应用
2.1 DESs-DLLME在农兽药残留检测中的应用
农兽药残留污染的准确分析检测是农产品质量安全管理的保证,简单可靠、灵敏度高和应用研究范围广的低成本检测技术是未来的发展趋势。FARAJZADEH等[16]最早将AA-DESs-DLLME结合气相色谱-氢火焰离子化检测器(gas chromatography-flame ionization detection,GC-FID)应用到果汁和蔬菜中9种农药的检测:190 μL准疏水性DESs(ChCl∶4-氯苯酚=1∶2,全文均为摩尔比)和5 mL样品溶液混合后,注入流速为300 mL/min的空气1 min,冰浴2 min,离心后取DESs相进行仪器分析;在最佳条件下,该方法的富集倍数为247~355,检出限为0.24~1.4 μg/L,回收率为49%~71%。该方法以空气代替分散剂的使用,成本低,操作简单,提取时间短,为今后DESs-DLLME在农药中的应用指明了新的方向。
在传统DESs-DLLME技术中,多使用IL或有机溶剂作为分散剂。最近,科研人员已将DESs作为分散剂或不使用分散剂。TORBATI等[27]以准疏水性DESs(ChCl∶丁酸=1∶2)为萃取剂,亲水性DESs[ChCl∶苯酚(phenol,Ph)=1∶3]为分散剂,利用DESs-DLLME结合气相色谱-质量选择检测器(mass selective detector,MS)测定干茶叶中6种除草剂,最佳条件下,富集倍数高达350~445,检出限为2.6~8.4 ng/kg,回收率为70%~89%。通过减少或不使用有机试剂,让DESs-DLLME技术更加绿色可持续,有望成为未来前处理技术中的新技术。
最初的DESs-DLLME技术仅限于一些简单的基质(以果汁、水体、食用油为代表),近年来,该技术已开始应用于复杂基质(以果蔬、蜂蜜和土壤为代表)。NASSER等[28]采用DESs-DLLME结合GC-MS检测蜂蜜中8种有机硫代磷酸盐农药,以三元相DESs(氯磷酸胆碱∶二氯乙酸∶癸酸=1∶1∶1)为萃取剂可极大降低DESs黏度,增加提取效率,乙腈为分散剂,最佳条件下富集因子为82~98,检出限为0.05~0.10 ng/g,回收率为82%~98%,符合农药残留检测标准。
在DESs-DLLME中,离心耗时且必不可少,在离心力的作用下可将含有目标物的DESs相沉积在离心管顶部或底部。最近的研究表明可以在DESs-DLLME中加入磁性材料,原位形成磁性DESs(magnetic deep eutectic solvents,MDESs),在外部磁铁的作用下实现无离心分离,减少萃取时间。PIAO等[29]提出in situ-MDESs-DLLME,并结合HPLC-UV检测大米中5种三嗪类除草剂:以DESs(四丁基氯化铵∶乙二醇=2∶1)为萃取溶剂,涡旋辅助萃取后加入磁性FeCl3和羰基铁粉,合成MDESs,利用磁铁的作用直接将MDESs从样品溶液中分离;最佳参数条件下检出限为1.49~3.10 ng/g,回收率为84.9%~117.5%。该方法绿色高效,且简化了萃取分离步骤。而JOUYBAN等[30]在萃取装置方面进行优化,提出DESs-DLLME结合GC-MS测定农民尿液和血浆中10种杀虫剂:利用特制双层玻璃容器,以DESs(薄荷醇∶苯乙酸=3∶1)为萃取溶剂,在氮气流的作用下,分散成微小液滴和实现对目标物的萃取富集,最后在外部冷水循环中凝聚。在最佳参数条件下,富集因子高达158~485,检出限为2~36 ng/L,回收率为79%~97%,该方法可实现无分散剂、无离心、无冰浴,适用于快速检测。
DESs-DLLME同样适用于兽药检测。JI等[31]首次将UA-DESs-DLLME结合HPLC-UVD测定果汁中3种磺胺类药物:以疏水性DESs(三辛基甲基氯化铵∶2-辛醇=1∶2)为萃取剂,最佳条件下检出限为0.02~0.05 μg/mL,回收率为88.09%~97.84%。该研究不需要使用分散剂,且和QuEChERs(quick,easy,cheap,effective,robust and safe extraction procedure)、固相萃取(solid phase extraction,SPE)等方法进行比较,操作过程简单、快速、环保,在食品基质的同类物质分析检测中具有重要的价值。
SHISHOV等[18]利用优化的EA-DESs-DLLME结合HPLC-MS/MS测定牛肝中酮洛芬和双氯酚酸:以准疏水性DESs(薄荷醇∶甲酸=1∶40)为萃取剂,目标物被萃取到DESs相中,然后加入Na2CO3溶液,DESs发生原位分解,薄荷醇萃取目标物,甲酸与Na2CO3作用产生CO2,促进目标物与薄荷醇的充分结合。在最佳条件下,富集因子为22~23,检出限为0.1~0.3 μg/kg,回收率为92%~108%。与标准的前处理技术相比,该方法可以显著缩小提取时间,技术指标均满足检测要求,在今后兽药的检测应用中具有潜在的价值。同时YU等[32]以疏水性DESs(癸酸∶甲基三辛基溴化铵=2∶1)为萃取溶剂,利用盐析辅助(salting out-assisted,SOA)-DESs-DLLME结合甲醇溶液反萃取,首次结合胶束电动毛细管色谱(micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography,MECC)测定牛奶、蜂蜜、水样中6种氟喹诺酮类抗生素。最佳参数条件下,富集因子高达531~858,检测限为0.006~0.010 μg/mL,回收率为87.8%~114.1%。
2.2 DESs-DLLME在真菌毒素检测中的应用
真菌毒素及其次生代谢物常见于食品中,例如:黄曲霉毒素和展青霉素,严重危害人体健康。当前,DESs-DLLME技术主要用于食用油、大米和果汁中真菌毒素的分析检测,但研究报道甚少。ALTUNAY等[26]首次提出UA-DESs-DLLME结合紫外可见分光光度仪(ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry,UV-Vis)测定果汁中展青霉素:以亲水性DESs(四丁基氯化铵∶2,3-丁二醇=1∶3)为提取剂,丙酮作为分散剂,最佳条件下检出限为2.2 μg/L,回收率为90.2%~106.9%。同时该方法同QuEChERs、基质分散固相萃取(matrix solid phase dispersion,MSPD)相比,精密度和回收率更好,线性范围不及MSPD,但优于QuEChERs。
HE等[33-34]对UA-DESs-DLLME进行了优化,结合HPLC-荧光检测器(fluorescence detection,FLD)测定大米和食用油中4种黄曲霉毒素:以亲水性DESs(ChCl∶丙二酸=1∶2)作为萃取剂,不需要分散剂和衍生化,在最佳条件下,检出限为0.000 5~0.06 μg/kg,回收率为72.05%~113.64%。与GB 5009.22—2016和欧盟标准相比,该方法更加简单、灵敏、高效,可作为食品基质中检测黄曲霉毒素的新方法。
2.3 DESs-DLLME在食品添加剂检测中的应用
食品添加剂在食品中广泛存在,但过量食用会对人体健康产生一定潜在危害。LIU等[35]首次应用UA-DESs-DLLME结合HPLC-UV测定食用油中叔丁基对苯二酚抗氧化剂,以亲水性DESs(ChCl∶乙二醇=1∶2)作为萃取剂,不需要分散剂,最佳条件下检测结果与传统方法相当。GE等[36]以疏水性DESs(DL-薄荷醇∶癸酸=2∶1)为萃取剂,应用in situ-DESs-DLLME结合HPLC-光电二极管检测器(diode array detector,DAD)测定水样中对羟基苯甲酸酯等4种防腐剂。最佳条件下,检出限为0.6~0.8 ng/mL,回收率为84.8%~108.7%,提供了一种用于在水溶液中检测防腐剂的新方法。最近,FARAJI [37]建立涡旋辅助DESs-DLLME-HPLC方法测定饮料、果冻、巧克力糖果中5种合成着色剂,以疏水性DESs(苄基三乙基氯化铵∶薄荷醇=1∶4)作为提取剂,富集倍数为95~10,检出限为0.01~0.08 μg/L,回收率为90%~97%。
近年来,工业染料违法添加到食品中的现象时有发生,科研人员为此开展了有关研究。SHI等[38]采用in situ-DESs-DLLME结合荧光分光光度计(fluorescence spectrophotometer,FLS)测定面条、鱼丸、蘑菇和纸杯中荧光增白剂52,以4-羟基苯甲酸-2-乙基己酯为萃取剂,在涡旋辅助条件下和目标物原位形成DESs,最佳条件下,检出限为0.045 μg/L,回收率为82~113%。同时OZAK等[39]以疏水性DESs(薄荷醇∶香豆素=1∶1)作为萃取剂,不需要分散剂,应用UA-DESs-DLLME结合HPLC-UV测定香料中4种苏丹红染料。优化相应参数,检出限为0.25~0.35 μg/g,回收率为85.55%~99.29%,该方法简单省时,价格低廉,环保,适合于快速检测大量样品。
2.4 DESs-DLLME在重金属元素检测中的应用
重金属元素由于排放或处理不当,容易对环境造成污染。DESs-DLLME常与石墨炉原子吸收(graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry,GFAAS)、电热原子吸收(electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry,ETAAS)、火焰原子吸收(flame atomic absorption spectrometry,FAAS)等联用检测重金属元素。YILMAZ等[40]提出UA-DESs-DLLME-FAAS测定水样中Cr3+和Cr6+,以亲水性DESs(ChCl∶Ph=1∶3)为萃取剂,二乙基二硫代氨基甲酸钠(sodium diethyldithiocarbamate,NaDDTC)为螯合剂,THF为分散剂,优化相应参数条件,该方法富集因子为20,检出限为5.5 μg/L,回收率为97%~109%。SOROURADDIN等[41]合成黏度可调的三元相DESs(薄荷醇∶山梨醇∶扁桃酸=1∶2∶1),且可用作螯合剂,甲醇为分散剂,结合DESs-DLLME-FAAS测定牛奶中Cd2+、Cu2+、Pb2+,最佳条件下回收率为88.8%~104.7%,检出限为0.38~0.42 μg/L。
近年来,DESs-DLLME技术开始集中于复杂基质中重金属元素的检测。TEKIN等[21]应用SA-DESs-DLLME结合开槽石英管(slotted quartz tube,SQT)-FAAS测定菩提茶中Co元素,以亲水性DESs(ChCl∶Ph=1∶2)为萃取剂,(Z)-3-溴代-5-((p-对甲基苯胺)甲基)苯酚为络合剂,THF作为分散剂,在最优条件下,检出限为2.0 μg/L,回收率为97.1%~100%,FAAS的检测能力提高了约67倍,与电感耦合等离子体质谱(inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry,ICP-MS)所测结果相当。HABIBOLLAHI等[24]利用VA-DESs-DLLME结合GFAAS测定土壤和蔬菜中Cd、Pb和Hg元素,以DESs(1-癸基-2,3-二甲基咪唑氯∶十一醇=1∶2)作为萃取剂,二乙基二硫代磷酸盐作为螯合剂,不需分散剂,含有目标物的DESs相在冰浴中凝固。优化相应参数,富集倍数高达114~172,检出限为0.01~0.03 g/kg,回收率为91%~110%,与浊点萃取(cloud point extraction,CPE)、SPE和传统DLLME相比,该方法线性范围广、简单、省时节能。
最近有研究建议将磁性碳纳米管(magnetic carbon nanotubes,MCNTs)加入到DESs中合成磁性纳米流体(magnetic nanofluid,MNF),利用MCNTs的超顺磁性和大比表面积等优势,可以实现自动化的无离心萃取过程。SHIRANI等[17]提出AA-DESs-MNF-DLLME结合ETAAS测定食品和非酒精饮料中Cd、Pb、Cu、As等重金属元素:以DESs(ChCl∶硫乙酰胺=1∶2)和MCNTs合成MNF作为萃取剂,不需要分散剂和螯合剂,在外磁铁的作用下,DESs-MNF从溶液中分离。优化相应参数,富集因子高达635~644.5,检出限为3~5.5 μg/L,回收率为94.4%~101.4%,该技术具有高灵敏度、操作过程简单、高通量、低溶剂消耗等优点,可应用于各种复杂基质中多种重金属元素的同时分析检测。
2.5 DESs-DLLME在其他污染物检测中的应用
TORBATI等[10]最早应用AA-DESs-DLLME检测水样中4种芳香胺,在10 mL样品溶液中,加入65 μL亲水性DESs(ChCl∶正丁酸=1∶2)和15 μL氯甲酸乙酯衍生剂,针筒来回抽吸溶液后形成乳浊液后离心冰浴,转移上层凝固相并用乙腈溶解,取1 μL溶液上GC-MS分析。该方法富集因子高达790~940,检测限为1.8~6.0 ng/L,回收率为79%~94%。与传统DLLME和顶空固相微萃取(Headspace-solid phase microextraction,HS-SPME)相比,该方法线性范围更广,富集倍数显著高于其他方法,这可能由于针筒来回抽吸使DESs分解成更微小的液滴,与目标物接触面积更大,萃取效率更高。
NAEBI等[42]首次在50 mL水样或饮料中添加0.69 g ChCl和2.8 mL油酸,在超声波辅助下原位形成疏水性DESs,并对2种抗氧化剂污染物(irganox 1010和irgaphos 168)进行萃取,不需要离心即可和溶液分层,最后进行HPLC-DAD分析。优化相应参数,富集因子高达435~488,检出限为0.03~0.09 ng/mL,回收率为74%~83%。研究人员将该方法同传统DLLME和IL-DLLME相比,该方法具有更好的富集倍数和回收率,且不需要使用有机溶剂和离心,更符合环保节能的要求。
DESs-DLLME同样可用于检测气体污染物。ZHANG等[43]应用VA-DESs-DLLME结合HPLC-DAD测定3种样品(鸭血、猪血、室内空气)中甲醛含量。样品溶液中先加入2,4-二硝基苯肼进行衍生化,后利用疏水性DESs(三辛基甲基氯化铵∶4-氰基苯酚=1∶1)进行萃取,不需要分散剂;最佳条件下检测限为0.2 μg/L,回收率为83.1%~104.4%。同其他前处理方法相比,该方法操作简单、成本低、提取时间短、且DES相与高效液相色谱流动相匹配良好。
3 结论和展望
与传统有机溶剂相比,DESs的优势在于蒸汽压低、热稳定性好、性质可调等性质;与IL相比,DESs更加廉价环保,DESs-DLLME技术已广泛被应用于重金属元素和化合物的分析检测,表2总结了DESs-DLLME在食品和环境污染物检测中的应用。然而,目前DESs-DLLME仍存在一些局限:(1)DESs的黏度较大,可能导致萃取效率较低,有时需借助辅助条件如涡旋,超声波等方式[5]或合成三元/四元相DESs[44-45],导致成本和步骤增加,且常用的疏水性DESs种类偏少[46];(2)有关不同DESs的萃取机理、动力学数据模型和稳定性研究较少,例如部分亲水性DESs(ChCl∶Ph)在萃取前后可能会发生分解,性质发生变化[47];(3) DESs的基因毒性研究缺乏,缺少系统的毒理学试验,限制DESs的应用[6, 48]。因此,为了促进DESs-DLLME的应用,今后应加强以下研究:(1)针对不同基质中不同目标物的性质,在加强DESs的毒性试验研究基础上,研发新的环保廉价、无毒、适用性更广更强、可生物降解的商用DESs;(2)研究不同DESs-DLLME模型在不同基质中的提取机理,优化提取工艺和技术参数,完善动力学数据模型,如应用集萃取、浓缩于一体的新型磁性纳米流体检测重金属元素[17],将DESs和磁性纳米管结合起来,简化操作步骤,提高萃取效率;(3)加强与不同的前处理方法相结合,例如DESs-DLLME-SPE[49]和QuEChERs-MA-DESs-DLLME[50]等技术,推广到更多复杂基质的应用;(4)研发微型、可自动化的DESs-DLLME技术,并加强与不同检测器和仪器之间的联用。综上,DESs-DLLME为食品及环境污染物的检测提供新途径,在缩短萃取时间、减少溶剂用量、节约操作成本和保持目标分子质量等方面比常规萃取技术具有竞争性优势。DESs随着研究的逐渐深入,相信DESs-DLLME技术在未来的应用将会更加环保、自动化、微型化。
表2 DESs-DLLME在食品和环境污染物检测中的应用
Table 2 Application of DESs-DLLME in the analysis of contaminants in food and environment
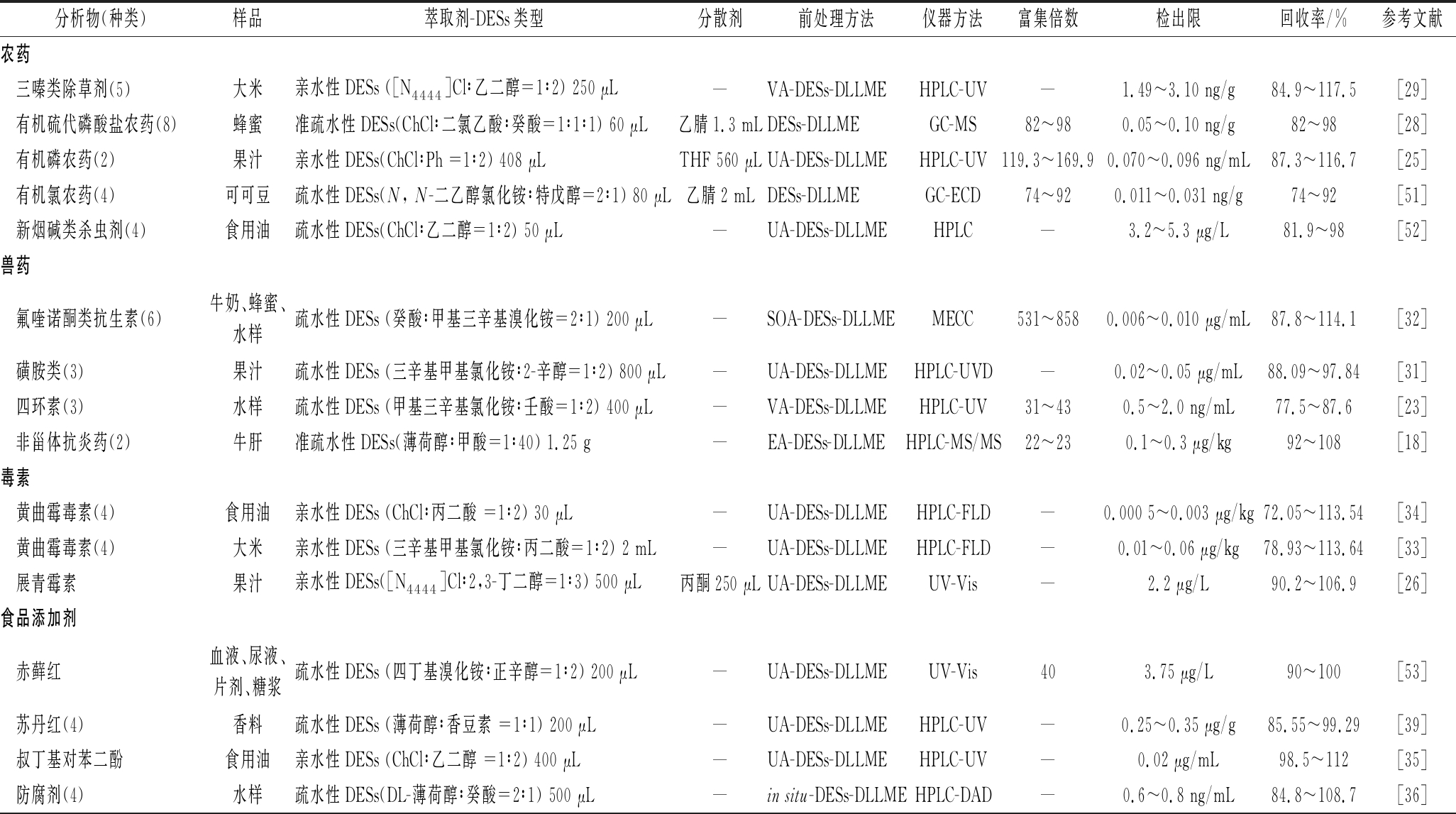
分析物(种类)样品萃取剂-DESs类型分散剂前处理方法仪器方法富集倍数检出限回收率/%参考文献农药三嗪类除草剂(5)大米亲水性DESs ([N4444]Cl∶乙二醇=1∶2) 250 μL—VA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-UV—1.49~3.10 ng/g84.9~117.5[29]有机硫代磷酸盐农药(8)蜂蜜准疏水性DESs(ChCl∶二氯乙酸∶癸酸=1∶1∶1) 60 μL乙腈1.3 mLDESs-DLLMEGC-MS82~980.05~0.10 ng/g82~98[28]有机磷农药(2)果汁亲水性DESs(ChCl∶Ph =1∶2) 408 μLTHF 560 μLUA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-UV119.3~169.90.070~0.096 ng/mL87.3~116.7[25]有机氯农药(4)可可豆疏水性DESs(N, N-二乙醇氯化铵∶特戊醇=2∶1) 80 μL乙腈2 mLDESs-DLLMEGC-ECD74~920.011~0.031 ng/g74~92[51]新烟碱类杀虫剂(4)食用油疏水性DESs(ChCl∶乙二醇=1∶2) 50 μL—UA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC—3.2~5.3 μg/L81.9~98[52]兽药氟喹诺酮类抗生素(6)牛奶、蜂蜜、水样疏水性DESs (癸酸∶甲基三辛基溴化铵=2∶1) 200 μL—SOA-DESs-DLLMEMECC531~8580.006~0.010 μg/mL87.8~114.1[32]磺胺类(3)果汁疏水性DESs (三辛基甲基氯化铵∶2-辛醇=1∶2) 800 μL—UA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-UVD—0.02~0.05 μg/mL88.09~97.84[31]四环素(3)水样疏水性DESs (甲基三辛基氯化铵∶壬酸=1∶2) 400 μL—VA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-UV31~430.5~2.0 ng/mL77.5~87.6[23]非甾体抗炎药(2)牛肝准疏水性DESs(薄荷醇∶甲酸=1∶40) 1.25 g—EA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-MS/MS22~230.1~0.3 μg/kg92~108[18]毒素黄曲霉毒素(4)食用油亲水性DESs (ChCl∶丙二酸 =1∶2) 30 μL—UA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-FLD—0.000 5~0.003 μg/kg72.05~113.54[34]黄曲霉毒素(4)大米亲水性DESs (三辛基甲基氯化铵∶丙二酸=1∶2) 2 mL—UA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-FLD—0.01~0.06 μg/kg78.93~113.64[33]展青霉素果汁亲水性DESs([N4444]Cl∶2,3-丁二醇=1∶3) 500 μL丙酮250 μLUA-DESs-DLLMEUV-Vis—2.2 μg/L90.2~106.9[26]食品添加剂赤藓红血液、尿液、片剂、糖浆疏水性DESs (四丁基溴化铵∶正辛醇=1∶2) 200 μL—UA-DESs-DLLMEUV-Vis403.75 μg/L90~100[53]苏丹红(4)香料疏水性DESs (薄荷醇∶香豆素 =1∶1) 200 μL—UA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-UV—0.25~0.35 μg/g85.55~99.29[39]叔丁基对苯二酚食用油亲水性DESs (ChCl∶乙二醇 =1∶2) 400 μL—UA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-UV—0.02 μg/mL98.5~112[35]防腐剂(4)水样疏水性DESs(DL-薄荷醇∶癸酸=2∶1) 500 μL—in situ-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-DAD—0.6~0.8 ng/mL84.8~108.7[36]
续表2
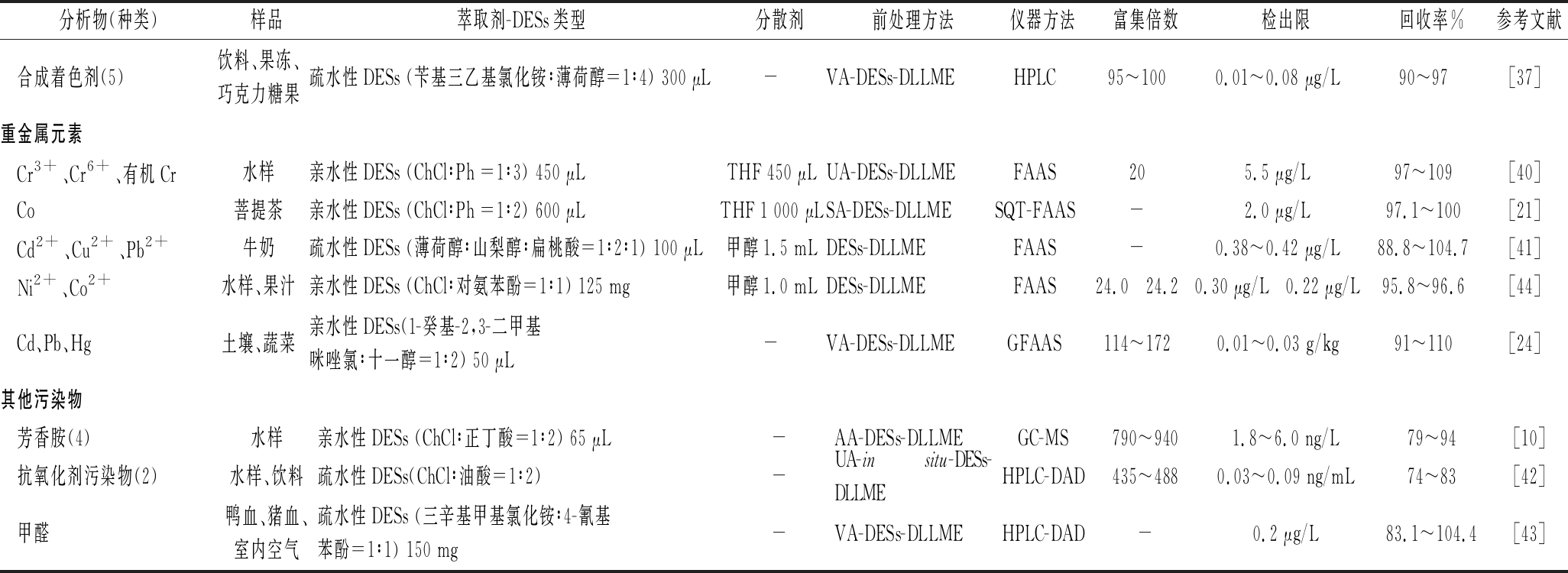
分析物(种类)样品萃取剂-DESs类型分散剂前处理方法仪器方法富集倍数检出限回收率%参考文献合成着色剂(5)饮料、果冻、巧克力糖果疏水性DESs (苄基三乙基氯化铵∶薄荷醇=1∶4) 300 μL-VA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC95~1000.01~0.08 μg/L90~97[37]重金属元素Cr3+、Cr6+、有机Cr水样亲水性DESs (ChCl∶Ph =1∶3) 450 μLTHF 450 μLUA-DESs-DLLMEFAAS205.5 μg/L97~109[40]Co菩提茶亲水性DESs (ChCl∶Ph =1∶2) 600 μLTHF 1 000 μLSA-DESs-DLLMESQT-FAAS-2.0 μg/L97.1~100[21]Cd2+、Cu2+、Pb2+牛奶疏水性DESs (薄荷醇∶山梨醇∶扁桃酸=1∶2∶1) 100 μL甲醇1.5 mLDESs-DLLMEFAAS-0.38~0.42 μg/L88.8~104.7[41]Ni2+、Co2+水样、果汁亲水性DESs (ChCl∶对氨苯酚=1∶1) 125 mg甲醇1.0 mLDESs-DLLMEFAAS24.0 24.20.30 μg/L 0.22 μg/L95.8~96.6[44]Cd、Pb、Hg土壤、蔬菜亲水性DESs(1-癸基-2,3-二甲基咪唑氯∶十一醇=1∶2) 50 μL-VA-DESs-DLLMEGFAAS114~1720.01~0.03 g/kg91~110[24]其他污染物芳香胺(4)水样亲水性DESs (ChCl∶正丁酸=1∶2) 65 μL-AA-DESs-DLLMEGC-MS790~9401.8~6.0 ng/L79~94[10]抗氧化剂污染物(2)水样、饮料疏水性DESs(ChCl∶油酸=1∶2) -UA-in situ-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-DAD435~4880.03~0.09 ng/mL74~83[42]甲醛鸭血、猪血、室内空气疏水性DESs (三辛基甲基氯化铵∶4-氰基苯酚=1∶1) 150 mg-VA-DESs-DLLMEHPLC-DAD-0.2 μg/L83.1~104.4[43]
[1] 张琰,张耀海,焦必宁.离子液体-分散液液微萃取在食品及环境污染物检测中的应用[J].食品科学,2015,36(5):250-259.
ZHANG Y,ZHANG Y H,JIAO B N.Application of ionic liquid-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of contaminants in foods and environment:A review[J].Food Science,2015,36(5):250-259.
[2] PAIVA A,CRAVEIRO R,AROSO I,et al.natural deep eutectic solvents-solvents for the 21 st century[J].ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2014,2(5):1 063-1 071.
[3] KHEZELI T,DANESHFAR A,SAHRAEI R.Emulsification liquid-liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent:An extraction method for the determination of benzene,toluene,ethylbenzene and seven polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2015,1 425:25-33.
[4] KARIMI M,DADFARNIA S,SHABANI A M H,et al.Deep eutectic liquid organic salt as a new solvent for liquid-phase microextraction and its application in ligandless extraction and preconcentraion of lead and cadmium in edible oils[J].Talanta,2015,144:648-654.
[5] LI G Z,ROW K H.Utilization of deep eutectic solvents in dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction[J].TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2019,120.DOI:10.1016/j.trac.2019.115651.
[6] LOMBA L,ZURIAGA E,GINER B.Solvents derived from biomass and their potential as green solvents[J].Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry,2019,18:51-56.
[7] LOOW Y L,NEW E K,YANG G H,et al.Potential use of deep eutectic solvents to facilitate lignocellulosic biomass utilization and conversion[J].Cellulose,2017,24(9):3 591-3 618.
[8] TORRES-VALENZUELA L S,BALLESTEROS-G MEZ A,RUBIO S.Green solvents for the extraction of high added-value compounds from agri-food waste[J].Food Engineering Reviews,2020,12(1):83-100.
MEZ A,RUBIO S.Green solvents for the extraction of high added-value compounds from agri-food waste[J].Food Engineering Reviews,2020,12(1):83-100.
[9] SMITH E L,ABBOTT A P,RYDER K S.Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications[J].Chemical Reviews,2014,114(21):11 060-11 082.
[10] TORBATI M,MOHEBBI A,FARAJZADEH M A,et al.Simultaneous derivatization and air-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of lighter than water deep eutectic solvent followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry:An efficient and rapid method for trace analysis of aromatic amines in aqueous samples[J].Analytica Chimica Acta,2018,1 032:48-55.
[11] OZAK S S,YILMAZ Y.Ultrasound-assisted hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent based solid-liquid microextraction of Sudan dyes in spice samples[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2020,236:118 353-118 360.
[12] JOUYBAN A,FARAJZADEH M A,KHOUBNASABJAFARI M,et al.Derivatization and deep eutectic solvent-based air-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction of salbutamol in exhaled breath condensate samples followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2020,191:113 572-113 578.
[13] NOROUZI F,KHOUBNASABJAFARI M,JOUYBAN-GHARAMALEKI V,et al.Determination of morphine and oxymorphone in exhaled breath condensate samples:Application of microwave enhanced three-component deep eutectic solvent-based air-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction and derivatization prior to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography B,2020,1152:122 256-122 262.
[14] ABDI K,EZODDIN M,PIROOZNIA N.Temperature-controlled liquid-liquid microextraction using a biocompatible hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for microextraction of palladium from catalytic converter and road dust samples prior to ETAAS determination[J].Microchemical Journal,2020,157:104 999-105 005.
[15] JIA L Y,HUANG X,ZHAO W F,et al.An effervescence tablet-assisted microextraction based on the solidification of deep eutectic solvents for the determination of strobilurin fungicides in water,juice,wine,and vinegar samples by HPLC[J].Food Chemistry,2020,317:126 424-126 430.
[16] FARAJZADEH M A,DABBAGH M S,YADEGHARI A.Deep eutectic solvent based gas-assisted dispersive liquid-phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography and flame ionization detection for the determination of some pesticide residues in fruit and vegetable samples[J].Journal of Separation Science,2017,40(10):2 253-2 260.
[17] SHIRANI M,HABIBOLLAHI S,AKBARI A.Centrifuge-less deep eutectic solvent based magnetic nanofluid-linked air-agitated liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry for simultaneous determination of cadmium,lead,copper,and arsenic in food samples and non-alcoholic beverages[J].Food Chemistry,2019,281:304-311.
[18] SHISHOV A,GERASIMOV A,NECHAEVA D,et al.An effervescence-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent decomposition:Determination of ketoprofen and diclofenac in liver[J].Microchemical Journal,2020,156:104 837-104 843.
[19] FARAJZADEH M A,HOJGHAN A S,MOGADDAM M R A.Development of a new temperature-controlled liquid phase microextraction using deep eutectic solvent for extraction and preconcentration of diazinon,metalaxyl,bromopropylate,oxadiazon,and fenazaquin pesticides from fruit juice and vegetable samples followed by gas chromatography-flame ionization detection[J].Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2018,66:90-97.
[20] BÜNYAMIN D,ADIL E,NAIL A.Determination of paracetamol in synthetic urea and pharmaceutical samples by shaker-assisted deep eutectic solvent microextraction and spectrophotometry[J].Microchemical Journal,2020,154.DOI:10.1016/j.microc.2020.104645.
[21] TEKIN Z,UNUTKAN T,ERULAS F,et al.A green,accurate and sensitive analytical method based on vortex assisted deep eutectic solvent-liquid phase microextraction for the determination of cobalt by slotted quartz tube flame atomic absorption spectrometry[J].Food Chemistry,2020,310:125 825-125 831.
[22] TORBATI M,FARAJZADEH M A,MOGADDAM M R A,et al.Development of microwave-assisted liquid-liquid extraction combined with lighter than water in syringe dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction using deep eutectic solvents:Application in extraction of some herbicides from wheat[J].Microchemical Journal,2019,147:1 103-1 108.
[23] DI X,ZHAO X J,GUO X L.Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent as a green extractant for high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of tetracyclines in water samples[J].Journal of Separation Science,2020,43(15):3 129-3 135.
[24] HABIBOLLAHI M H,KARIMYAN K,ARFAEINIA H,et al.Extraction and determination of heavy metals in soil and vegetables irrigated with treated municipal wastewater using new mode of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on the solidified deep eutectic solvent followed by GFAAS[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2019,99(2):656-665.
[25] HEIDARI H,GHANBARI-RAD S,HABIBI E.Optimization deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction by using the desirability function approach for extraction and preconcentration of organophosphorus pesticides from fruit juice samples[J].Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2020,87:103 389-103 395.
[26] ALTUNAY N,ELIK A,GÜRKAN R.A novel,green and safe ultrasound-assisted emulsification liquid phase microextraction based on alcohol-based deep eutectic solvent for determination of patulin in fruit juices by spectrophotometry[J].Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2019,82:103 256-103 264.
[27] TORBATI M,FARAJZADEH M A,MOGADDAM M R A,et al.Deep eutectic solvent based homogeneous liquid-liquid extraction coupled with in-syringe dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction performed in narrow tube;Application in extraction and preconcentration of some herbicides from tea[J].Journal of Separation Science,2019,42(9):1 768-1 776.
[28] NASSER M,MOHAMMADALI T,ALI F M,et al.Synthesis and characterization of phosphocholine chloride-based three-component deep eutectic solvent:Application in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for determination of organothiophosphate pesticides[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(6):2 364-2 371.
[29] PIAO H L,JIANG Y X,QIN Z C,et al.Application of an in-situ formulated magnetic deep eutectic solvent for the determination of triazine herbicides in rice[J].Talanta,2021,222:121 527-121 533.
[30] JOUYBAN A,FARAJZADEH M A,AFSHAR MOGADDAM M R.Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of deep eutectic solvent droplets for analysis of pesticides in farmer urine and plasma by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography B,2019,1 124:114-121.
[31] JI Y H,MENG Z R,ZHAO J,et al.Eco-friendly ultrasonic assisted liquid-liquid microextraction method based on hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for the determination of sulfonamides in fruit juices[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2020,1 609:460 520-460 529.
[32] YU K L,YUE M E,XU J,et al.Determination of fluoroquinolones in milk,honey and water samples by salting out-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent combined with MECC[J].Food Chemistry,2020,332:127 371-127 377.
[33] HE T T,ZHOU T,WAN Y Q,et al.A simple strategy based on deep eutectic solvent for determination of aflatoxins in rice samples[J].Food Analytical Methods,2020,13(2):542-550.
[34] HE T T,ZHOU T,WAN H,et al.One-step deep eutectic solvent strategy for efficient analysis of aflatoxins in edible oils[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(13):4 840-4 848.
[35] LIU W,ZHANG K D,YU J J,et al.A green ultrasonic-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent for the HPLC-UV determination of TBHQ in edible oils[J].Food Analytical Methods,2017,10(9):3 209-3 215.
[36] GE D D,WANG Y,JIANG Q,et al.A deep eutectic solvent as an extraction solvent to separate and preconcentrate parabens in water samples using in situ liquid-liquid microextraction[J].Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society,2019,30(6):1 203-1 210.
[37] FARAJI M.Determination of some red dyes in food samples using a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent-based Vortex assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2019,1 591:15-23.
[38] SHI Y Y,LI X,SHANG Y,et al.Effective extraction of fluorescent brightener 52 from foods by in situ formation of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent[J].Food Chemistry,2020,311:125 870-125 876.
[39] OZAK S S,YILMAZ Y.Ultrasound-assisted hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent based solid-liquid microextraction of Sudan dyes in spice samples[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2020,236:118 353-118 360.
[40] YILMAZ E,SOYLAK M.Ultrasound assisted-deep eutectic solvent based on emulsification liquid phase microextraction combined with microsample injection flame atomic absorption spectrometry for valence speciation of chromium(III/VI) in environmental samples[J].Talanta,2016,160:680-685.
[41] SOROURADDIN S M,FARAJZADEH M A,DASTOORI H.Development of a dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method based on a ternary deep eutectic solvent as chelating agent and extraction solvent for preconcentration of heavy metals from milk samples[J].Talanta,2020,208:120 485-120 492.
[42] NAEBI M,JAMSHIDI M A,FARAJZADEH M A,et al.In-process prepared deep eutectic solvent based homogeneous liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of irgaphos 168 and irganox 1010 in polypropylene packed drinks[J].Journal of Separation Science,2020,43(14):2 850-2 857.
[43] ZHANG K,LIU C,LI S Y,et al.A hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent based vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of formaldehyde from biological and indoor air samples by high performance liquid chromatography[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2019,1589:39-46.
[44] SOROURADDIN S M,FARAJZADEH M A,OKHRAVI T.Development of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent using as complexing agent and extraction solvent:Application for extraction of heavy metals[J].Separation Science and Technology,2020,55(16):2 955-2 966.
[45] ALOTHMAN Z A,HABILA M A,YILMAZ E,et al.A novel deep eutectic solvent microextraction procedure for enrichment,separation and atomic absorption spectrometric determination of palladium at ultra-trace levels in environmental samples[J].Measurement,2020,153:107 394-107 398.
[46] FLORINDO C,BRANCO L C,MARRUCHO I M.Quest for green-solvent design:From hydrophilic to hydrophobic (deep) eutectic solvents[J].Chemsuschem,2019,12(8):1 549-1 559.
[47] SHISHOV A,GORBUNOV A,MOSKVIN L,et al.Decomposition of deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride and phenol in aqueous phase[J].Journal of Molecular Liquids,2020,301:112 380-112 384.
[48] CELEBI A T,VLUGT T J H,MOULTOS O A.Structural,thermodynamic,and transport properties of aqueous reline and ethaline solutions from molecular dynamics simulations[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2019,123(51):11 014-11 025.
[49] MARYAM S,HAKIM F,HAMIDREZA S,et al.Sustainable and green microextraction of organophosphorus flame retardants by a novel phosphonium-based deep eutectic solvent[J].Journal of Separation Science,2020,43(2):452-461.
[50] FARAJZADEH M A,SOHRABI H,MOHEBBI A,et al.Combination of a modified quick,easy,cheap,efficient,rugged,and safe extraction method with a deep eutectic solvent based microwave-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction:Application in extraction and preconcentration of multiclass pesticide residues in tomato samples[J].Journal of Separation Science,2019,42(6):1 273-1 280.
[51] ASGHAR M,AFSHAR M M R,ALI F M,et al.A three-phase solvent extraction system combined with deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for extraction of some organochlorine pesticides in cocoa samples prior to gas chromatography-electron capture detector[J].Journal of Separation Science,2020,43(18):3 674-3 682.
[52] 王素利, 郭振幅,庚丽丽.基于低共熔溶剂的液-液微萃取技术测定食用油中的新烟碱类杀虫剂[J/OL].食品科学,2020.
WANG S L,GUO Z F,GENG L L.The liquid phase microextraction technology based on deep eutectic solvent for determination of new neonicotinoid insecticide in edible oil[J/OL].Food Science,2020.
[53] YUVALI D,SEYHANEYILDIZI M,SOYLAK M,et al.An environment-friendly and rapid liquid-liquid microextraction based on new synthesized hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for separation and preconcentration of erythrosine (E127) in biological and pharmaceutical samples[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2021,244:118 842-118 847.